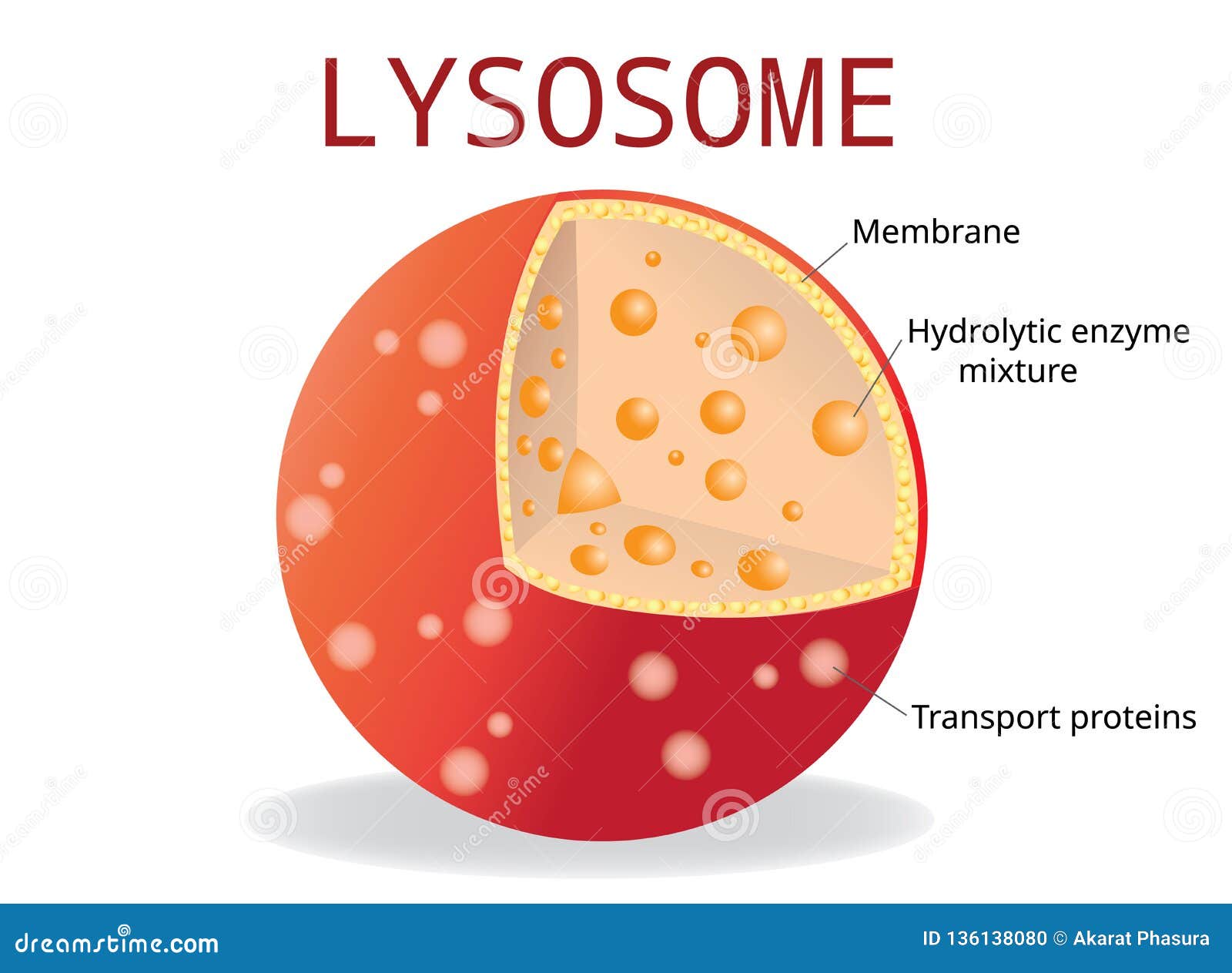
Structure lysosomes infographics Royalty Free Vector Image

STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS OF LYSOSOMES
Quick look: Lysosomes are membrane bounded organelles found in animal and plant cells. They vary in shape, size and number per cell and appear to operate with slight differences in cells of yeast, higher plants and mammals. Lysosomes contribute to a dismantling and re-cycling facility.
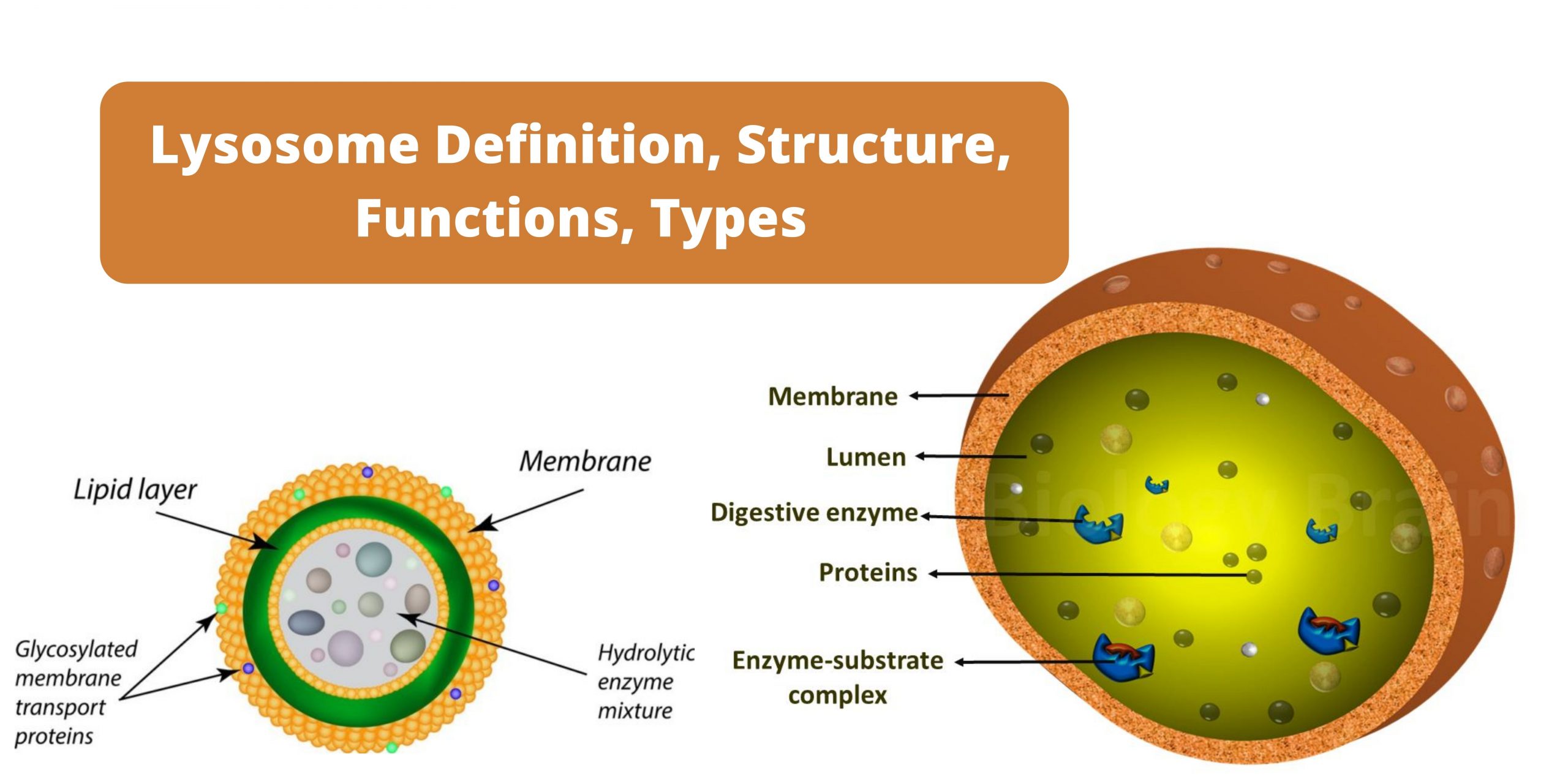
Lysosome Definition, Structure, Functions, Types
The lysosomes show polymorphism in different cell types. There are two basic types of lysosomes. Golgi complex buds off primary lysosomes containing hydrolytic enzymes. The vacuole or phagosome arising by endocytosis associates and fuses with primary lysosome to form secondary lysosome (Fig. 2.61).

What is a Lysosome? (with pictures)
A quick overview The lysosomes are small organelles that work as the recycling center in the cells. They are membrane-bounded spheres full of digesting enzymes.

Structure lysosomes infographics Royalty Free Vector Image
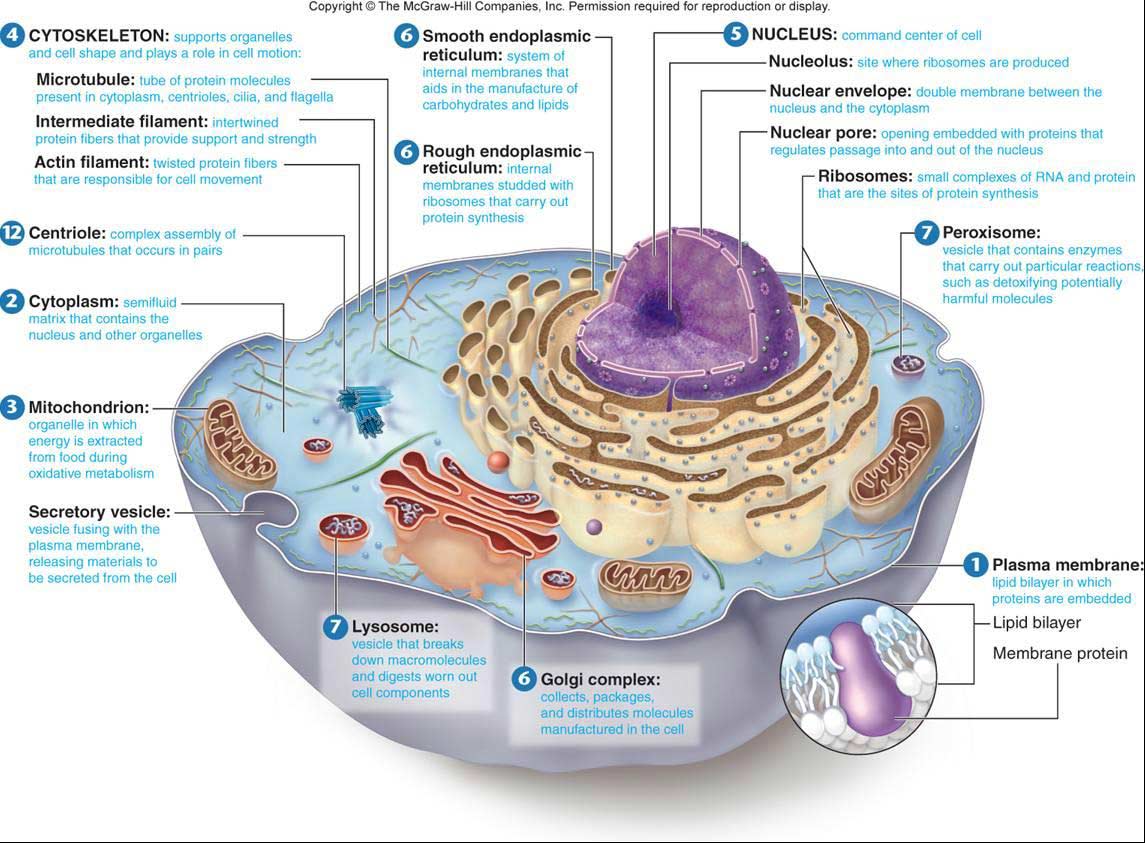
Key points: All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in and comes out. The cell membrane surrounds a cell's cytoplasm, which is a jelly-like substance containing the cell's parts. Cells contain parts called organelles. Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell.

Lysosome anatomy stock vector. Illustration of structure 185705801
lysosome, subcellular organelle that is found in nearly all types of eukaryotic cells (cells with a clearly defined nucleus) and that is responsible for the digestion of macromolecules, old cell parts, and microorganisms. Each lysosome is surrounded by a membrane that maintains an acidic environment within the interior via a proton pump.
Lysosomes Definition, Structure, Formation, Functions, Types and Diagram
A lysosome is a membrane-bound cell organelle that contains digestive enzymes. Lysosomes are involved with various cell processes. They break down excess or worn-out cell parts. They may be used to destroy invading viruses and bacteria.
The Structure of Lysosomes. Infographics. Vector Illustration Stock Vector Illustration of
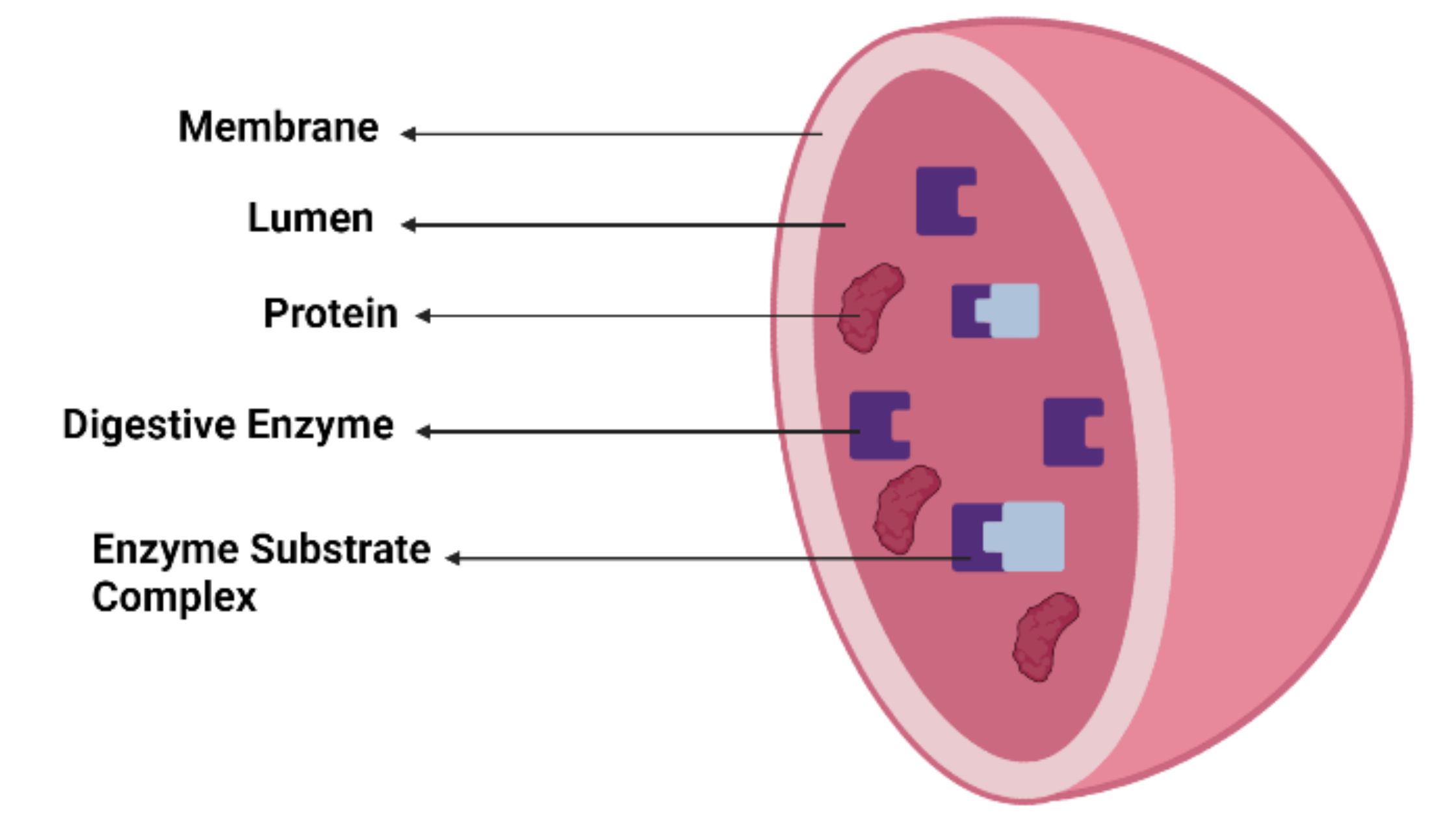
The diagram below shows the lysosome structure within a cell. Lysosome diagram showcasing enzyme complexes within the single-walled membrane The pH level of the lumen lies between 4.5 and 5.0, which makes it quite acidic. It is almost comparable to the function of acids found in the stomach.

Lysosome In Plant Cell Description Raine AP Biology Chapter 6 / To the tasks
Like it? Share it! Lysosomes are called the stomach of cells. Their main function is to carry enzymes that are developed by the cell. This BiologyWise article explains the structure, location, and function of lysosomes. The human body comprises about 50 to 75 trillion cells.

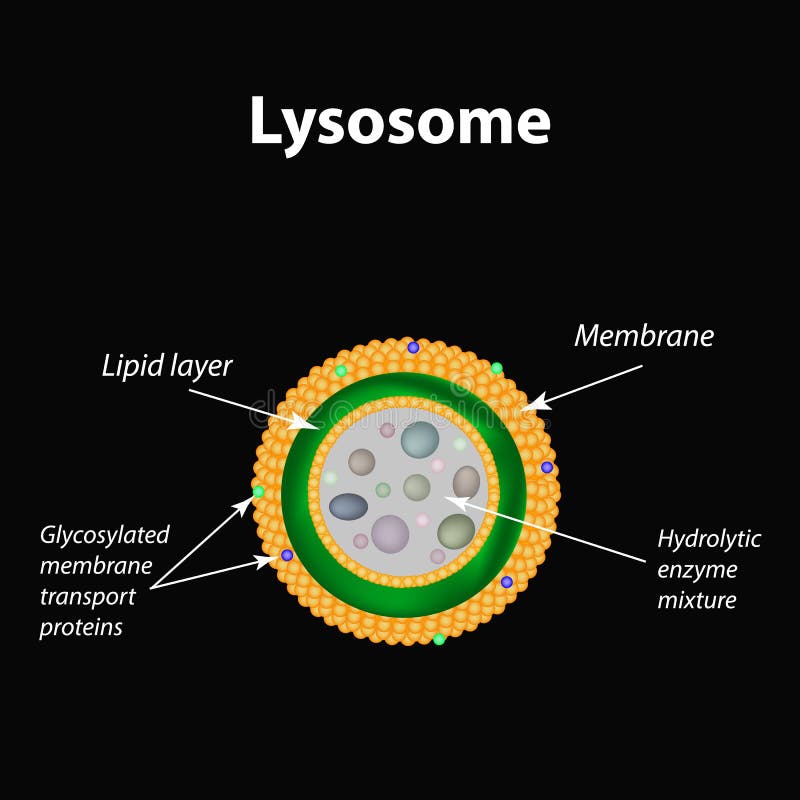
The structure of lysosomes Infographics Royalty Free Vector
Lysosomal biology and function: modern view of cellular debris bin is a review article that summarizes the recent advances in understanding the roles of lysosomes in various cellular processes, such as metabolism, autophagy, immunity and aging. The article also discusses the implications of lysosomal dysfunction in human diseases and potential therapeutic strategies. The article provides a.

Lysosome Description, Formation, & Function Cells activity, Plant cell model, What is cell
Home Cell Biology Lysosomes: Definition, Structure, Functions Animesh Sahoo November 12, 2021 Lysosomes are tiny vascular membrane-bound vesicles involved in intracellular digestion. They contain a variety of hydrolytic enzymes that remain active under acidic conditions. Greek words " Lysis = digestive or break down, and soma = body ".
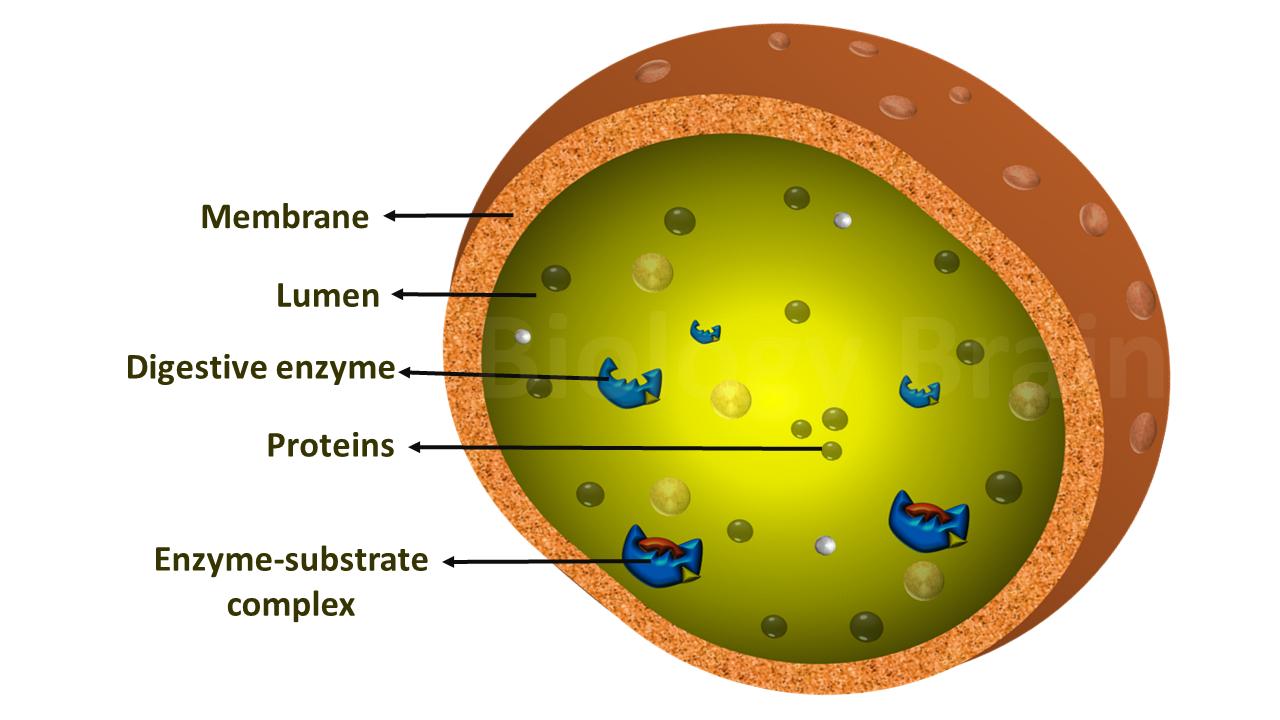
Diagram of Lysosomes and Types Biology Brain
Electron micrograph of lysosomes and mitochondria in a mammalian cell. Lysosomes are indicated by arrows. (Visuals Unlimited/K. G. Murti.) Go to: Lysosomal Acid Hydrolases Lysosomes contain about 50 different degradative enzymes that can hydrolyze proteins, DNA, RNA, polysaccharides, and lipids.
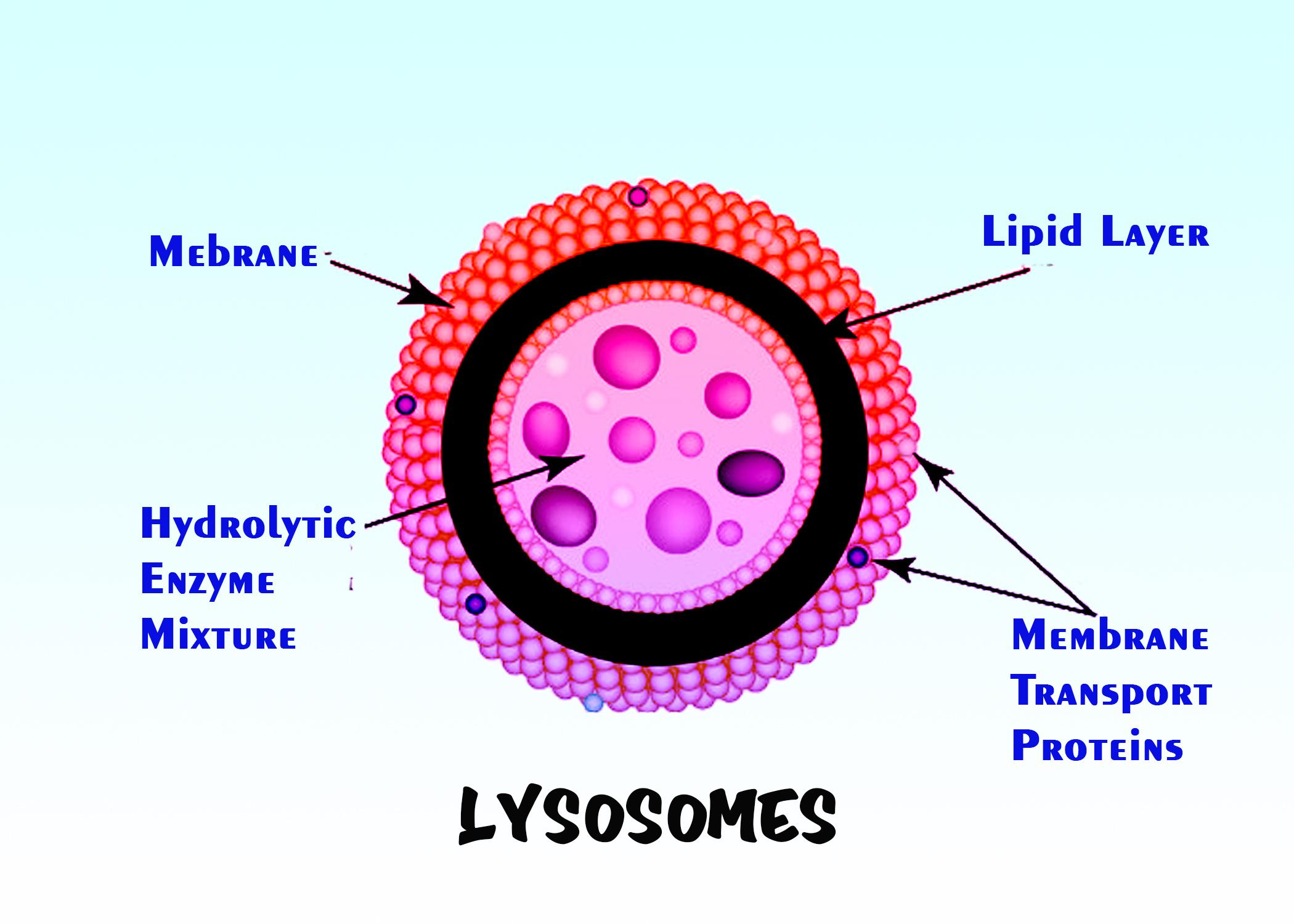
Useful Notes on the Four Kinds of Lysosomes Biology
Lysosomes Diagram Table of Contents Structure of Lysosomes Lysosomal Enzymes Lysosomal Membrane Types of Lysosomes A. Primary Lysosomes B. Heterophagosomes C. Autophagosomes D. Residual Bodies Functions of Lysosomes Presence of Lysosomes Presence of Lysosomes in the Animal tissue Presence of lysosome in the Protozoa Presence of lysosome in Plants
Lysosomes are practically present in all cells except(A) WBC(B) RBC(C) Epithelial cells(D
The endomembrane system ( endo - = "within") is a group of membranes and organelles in eukaryotic cells that works together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins.
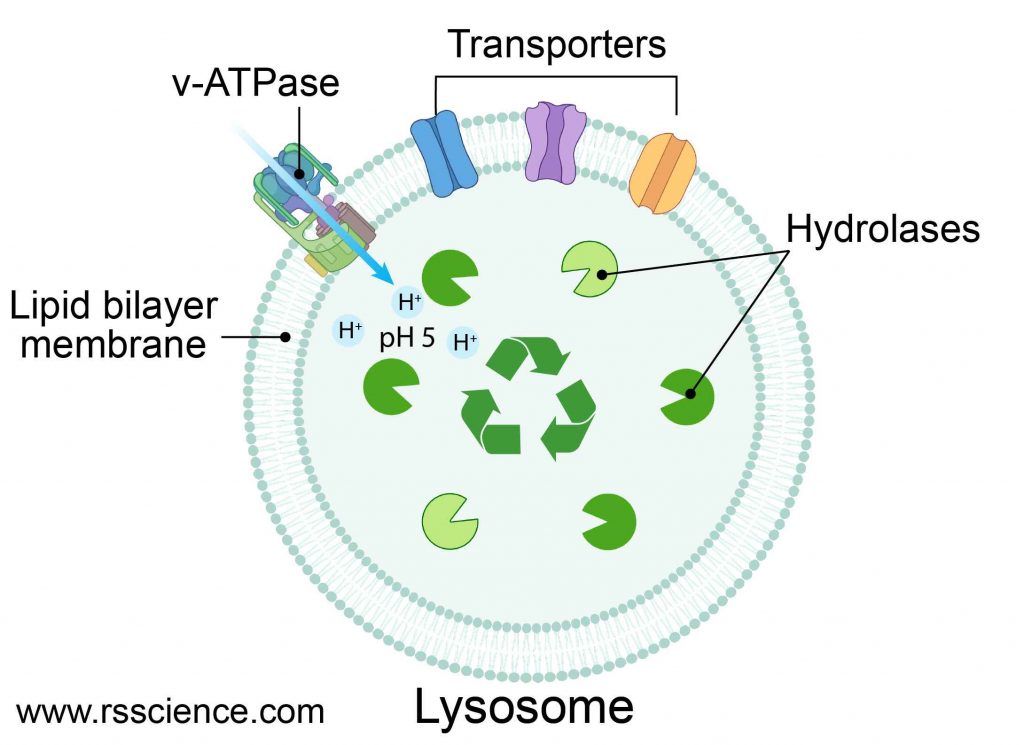
Lysosome the cell’s recycling center definition, structure, function, and biology
Vesicles and Vacuoles. Vesicles and vacuoles are membrane-bound sacs that function in storage and transport. Vacuoles are somewhat larger than vesicles, and the membrane of a vacuole does not fuse with the membranes of other cellular components. Vesicles can fuse with other membranes within the cell system ( Figure 5.11.1 5.11. 1 ).
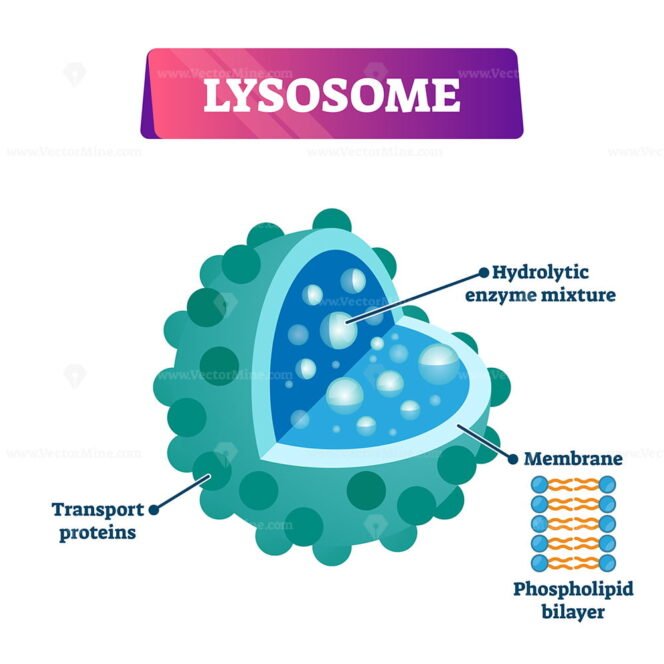
Lysosome cell organelle vector illustration labeled cross section diagram VectorMine
A lysosome ( / ˈlaɪsəˌsoʊm /) is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. [1] They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that digest many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane proteins and its lumenal proteins.
Plant Cell Lysosome Is What Are Lysosomes and How Are They Formed? / Cell membrane is the
Lysosomes: Structure, Forms, Functions and Other Details (With Diagram) Article Shared by ADVERTISEMENTS: The existence of lysosomes was subtly suggested for the first time in the early 1950s by a series of experiments carried out by Nobel Prize Laureate Christian de Duve and his co-workers.