Overview of SAP NetWeaver AS ABAP

Beginners Guide To ABAP Module 1 SAP System Architecture
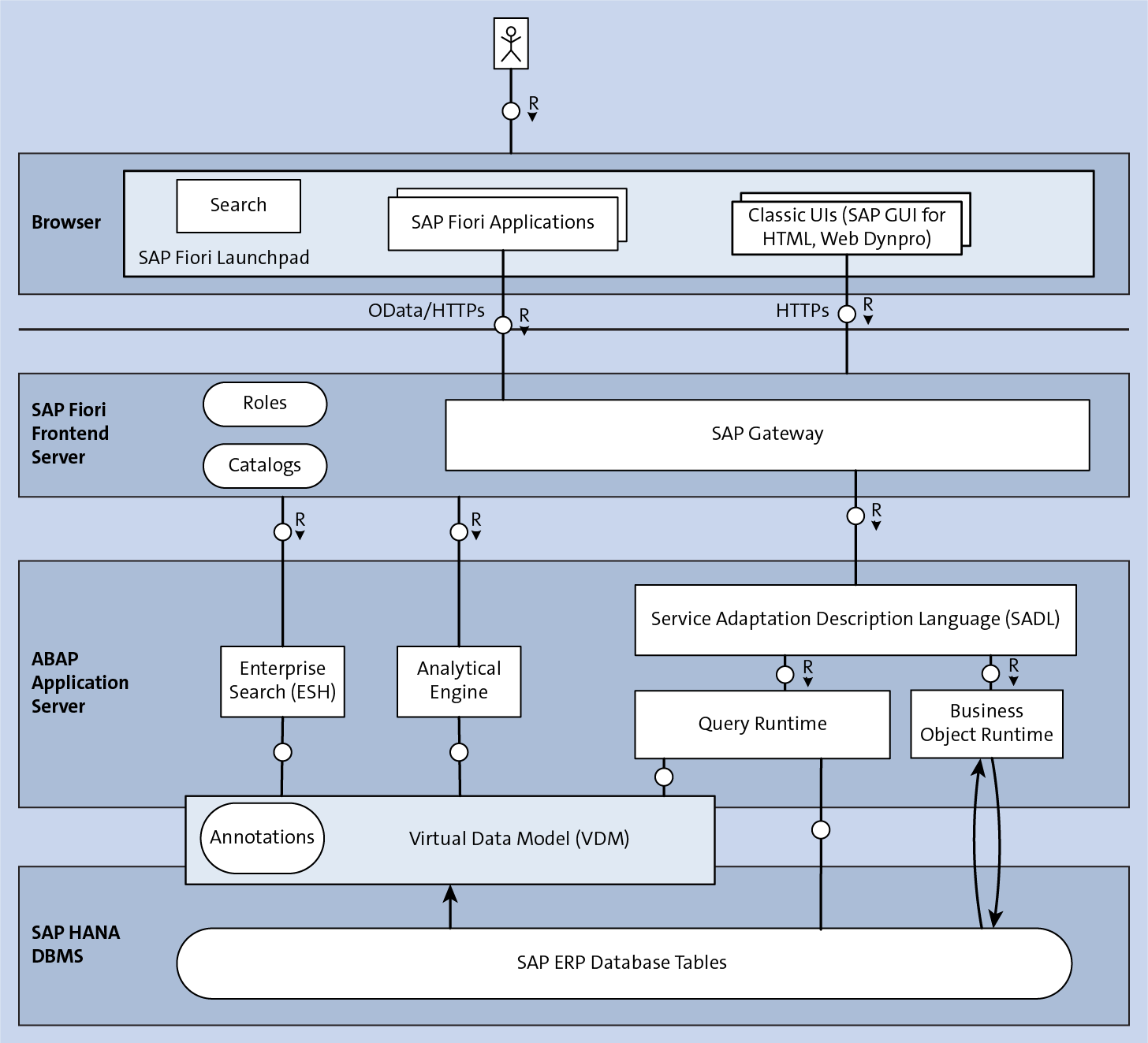
On this page. Application Server ABAP (AS ABAP) provides a complete infrastructure for developing and running ABAP-based applications. The design of AS ABAP is aimed at providing an exceptionally high level of robustness and supportability for the applications running on it. The architecture of AS ABAP and basic terminology are explained below.

ABAP Application Server
ABAP Keyword Documentation → ABAP Glossary →. Application layer. Software layer of an AS ABAP in which application programs are executed. The application layer is realized from exactly one message server and one or more application servers, on which ABAP programs are executed.
What is SAP HANA? A Guide to InMemory Computing with SAP SAP PRESS
An SAP application layer that's located through availability sets in the same network spine as the SAP Central services (ASCS/SCS) VM or VMs. Note Because you deploy one DBMS and ASCS/SCS VMs into one zone and the second DBMS and ASCS/SCS VMs into another zone to create a high availability configurations, you'll need a different proximity placement group for each of the zones.

A little knowledge is a dangerous thing SAP Blogs
The enterprise manage layer is based on SAP Best Practices and offers preconfigured end-to-end business processes across all application areas, including sample master data and print forms as well as detailed documentation for users. Its main value however lies in the preconfigured Finance processes that are specific to multinational corporations:

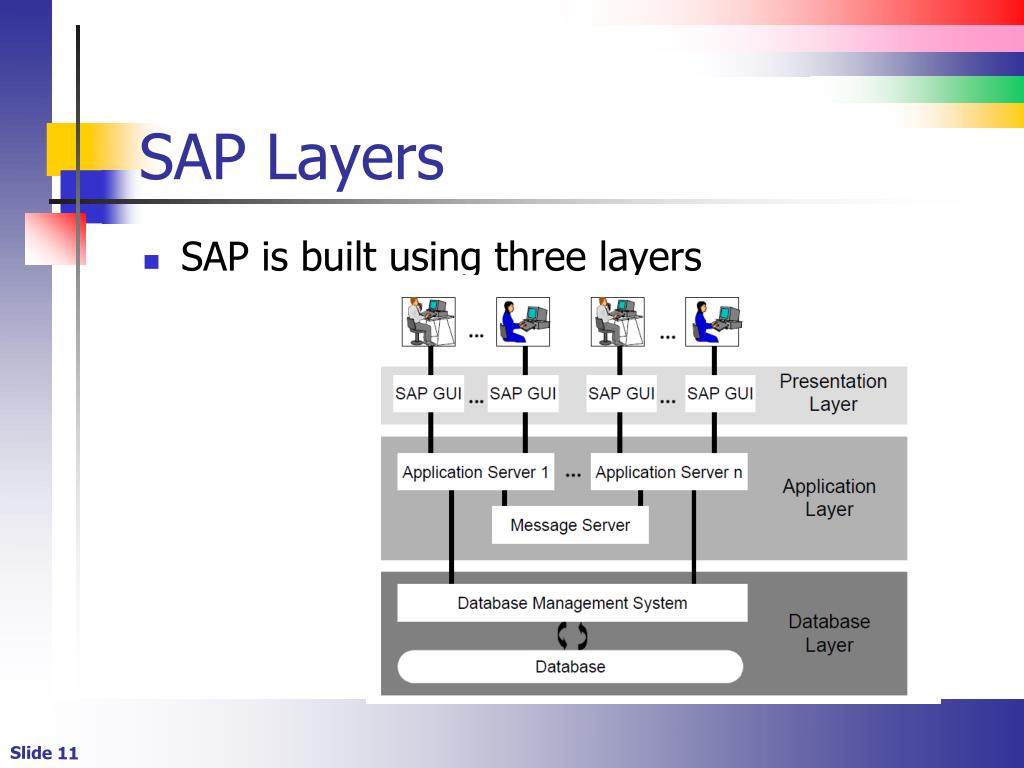
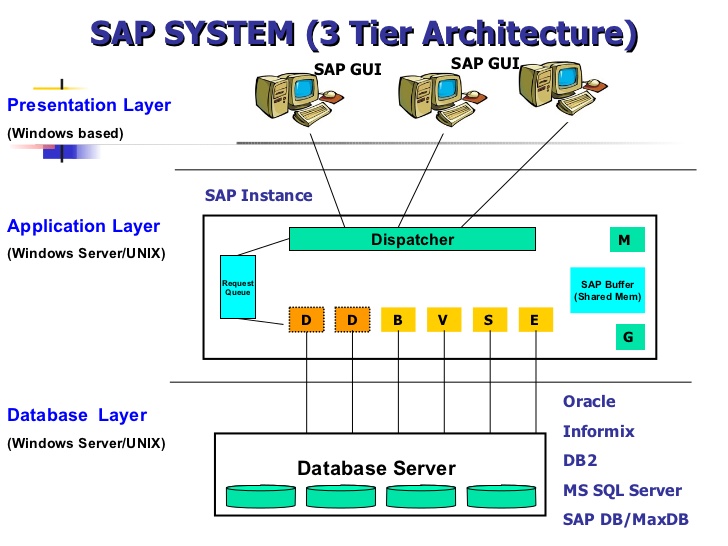
SAP R/3 Architecture has three layers Presentation Layer,Application Layer,Database Layer.SAP R
The database-dependent layer in the diagram serves to hide the differences between database systems from the rest of the database interface.. In SAP NetWeaver Application Server, you may only have one lock table. You may therefore also only have one ABAP application server with enqueue work processes. Normally, a single enqueue work process.

SAP Architecture Detailed Explanation (2023)
What is The Application Layer in SAP R/3 Architecture? The Application Layer is a central and critical component of SAP R/3 architecture. It plays a pivotal role in ensuring the seamless execution of business processes and the overall functionality of the ERP system. Below, we will delve into the purposes and functions of the Application Layer.

SAP Application Interface Framework All You Need to Know About SAP AIF SAP Blogs
An Environment, and more specifically a Shared Environment, is a virtual location within your SAP Build Process Automation subscription where projects are deployed. In deployed projects you can use artifacts, such as triggers, workflow definitions, API keys… and can assign resources such as Agents. The output of these artifacts are automation.

SAP Basis Services SAP Administration Full SAP System Maintenance
The infrastructure layer of a region is either provided by SAP or by one of SAP's Instrastructure as a Service (IaaS) partners Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Alibaba Cloud.. Java, and SAP HANA extended application services (SAP HANA XS) applications. You can also use the UI Development Toolkit.

S/4HANA for Customer Management 1.0 introduction from technical point of view SAP Blogs
Yes! The enterprise management layer is a standard SAP S/4HANA system (on premise). You can access the IMG with SAP GUI and make the configuration changes or additions you need. We recommend you keep client 050 as-is for future reference though and do not change configuration nor master data there.

SAP Architecture Detailed Explanation (2023)
Application Link - A link between elements in an application layer diagram. See Application Links (EAM). Program - A high-level EA initiative. See Programs, Projects, and Phases (EAM). Project - An EA initiative. See Programs, Projects, and Phases (EAM). Impact - A link from an EA initiative to the asset that it impacts.
PPT Summary of The SAP Ecosystem and Functional Software PowerPoint Presentation ID5803776
Application Layer is also known as Kernel Layer and Basic Layer. SAP application programs are executed in Application Layer. Application Layer serves as a purpose of a communicator between Presentation and Database Layer. Application server is where the dispatcher distributes the work load to the different work processes makes the job done.
SAP BASIS FROM BASIC SAP Architecture
The structure, designed to provide flexibility and capacity to businesses of all sizes, is a major and critical feature of SAP R/3.SAP R/3 architecture is based on a three-tiered client-server model that includes an interface layer, an application layer, and an application layer. Definition of SAP R/3 Architecture. R3 means real-time.

Overview of the Architecture of SAP BW
The application layer and presentation layer components can be distributed across any number of hosts. It is also possible to install more than one ABAP application server on a single host. A common configuration is to run the database system and a single ABAP application server (containing special database services) on one host, and to run each further application server on its own host.

Composite Application Layers
Learn how to use the SAP Cloud Platform Integration File Adapter to read and write files from the application layer of the SAP system. This document provides a detailed guide on the configuration, parameters, and features of the File Adapter.

Overview of SAP NetWeaver AS ABAP
To better grasp the SAP architecture, let's look at these three elements in more detail. The SAP System Architecture consists of the Presentation, Application, and Database layers. 1. Presentation Layer. The presentation layer is responsible for the user experience and for making sure that the SAP system is responsive and easy to interact with.

SAP S/4HANA EndtoEnd Performance SAP Blogs
This layer is the interface between the R/3 System and its users. The R/3 System uses the SAPgui to provide an intuitive graphical user interface for entering and displaying data. The presentation layer sends the user's input to the application server, and receives data for display from it. While a SAPgui component is running, it remains.