Yield Strength vs. Tensile Strength 6 Key Differences, Pros & Cons, Examples Difference 101
What is Yield in Materials? Yield Stress, Yield Strength, and Yield Point Materials Science
A fastener's tensile strength, or ultimate tensile strength, is the force at which the fastener fractures. To test tensile strength, we use a wedge tensile test, where a wedge is placed under the head of the fastener, and force is applied until the fastener breaks.

Yield Strength vs. Tensile Strength 6 Key Differences, Pros & Cons, Examples Difference 101
Like yield strength, tensile strength is expressed in units of pressure, such as Pascals (Pa) or pounds per square inch (psi). The ultimate tensile strength of a material can be found on a stress-strain curve, which plots the applied stress against the resulting strain. The peak of this curve represents the material's tensile strength, and.

Difference between Yield Strength and Ultimate Strength YouTube
Yield strength refers to the point at which a material undergoes permanent deformation or a significant change in shape due to applied stress, signaling its transition from elastic to plastic behavior. On the other hand, tensile strength represents the maximum amount of stress a material can withstand before it fractures or breaks.
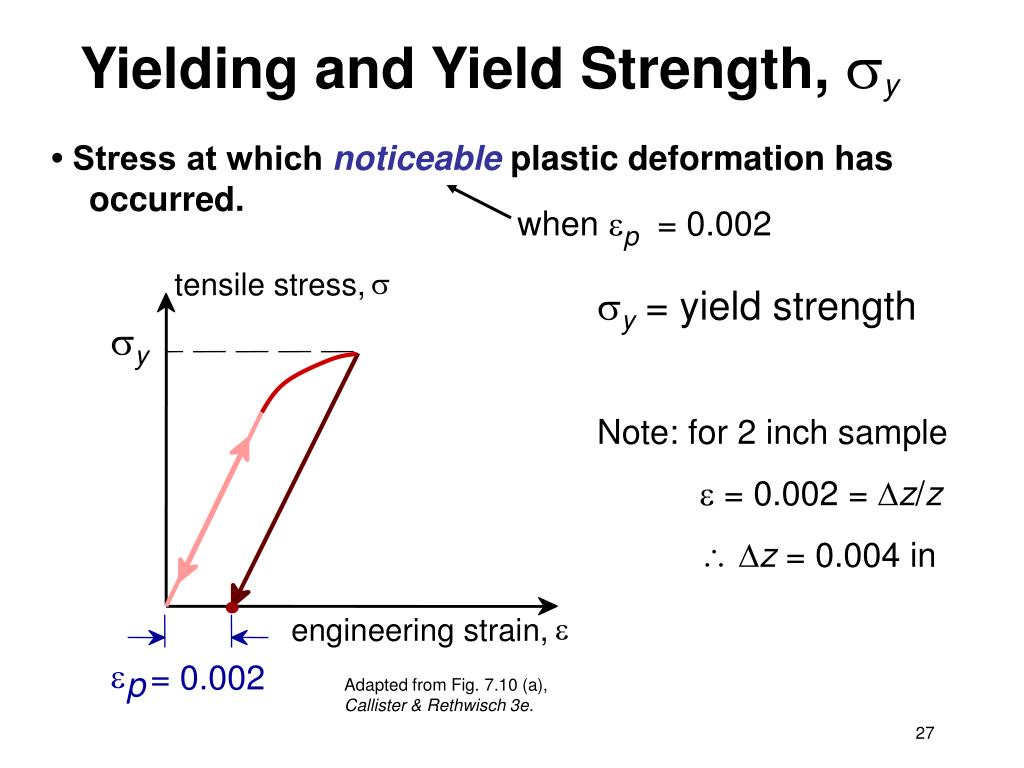
PPT Chapter 7 機械性質 ( Mechanical Properties) PowerPoint Presentation ID3596603
#yieldstrength #tensilstrength #metals #materials Visit https://link.matmatch.com/eqmat to find equivalent materialsVisit https://link.matmatch.com/EMtoMM to.
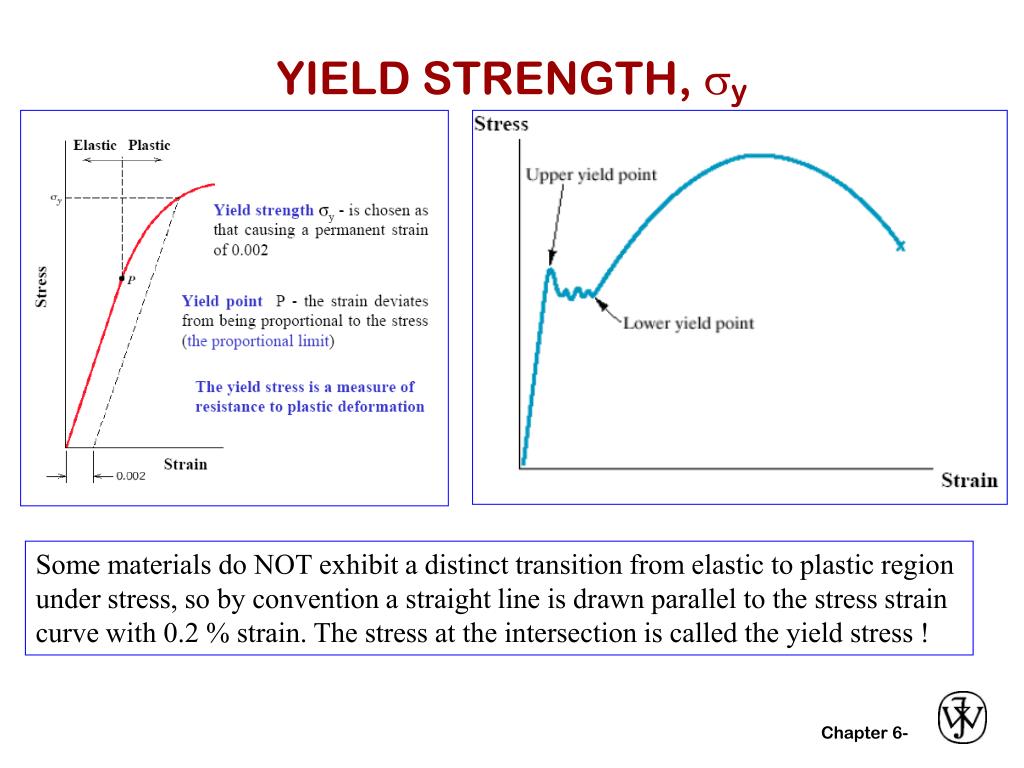
PPT CHAPTER 6 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID453043
The tensile strength and yield strength of a metal decide its areas of application. In the case of larger projects, such as in the aerospace or construction industries, these factors are a matter of life or death. Designers make sure that the maximum stress never reaches the yield strength of the metal used.
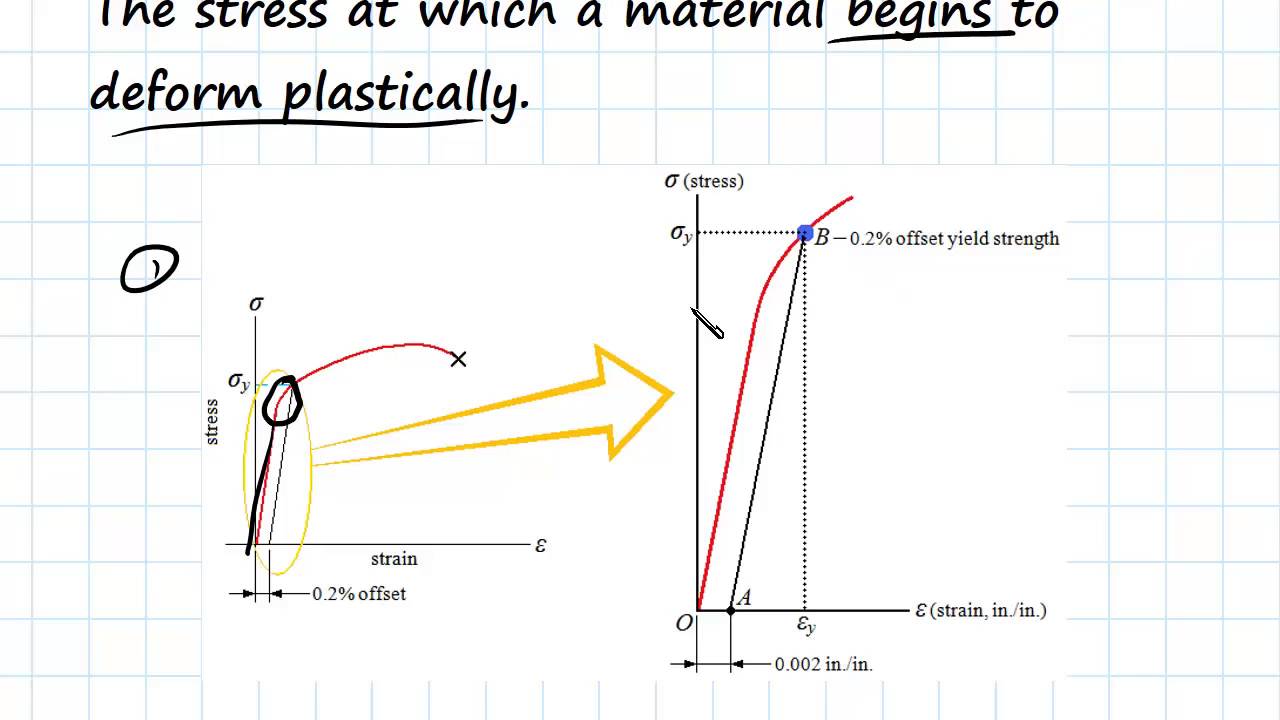
Yield and Tensile Strength Engineering Materials YouTube
Yield Strength vs Tensile Strength. Tensile strength quantifies the force needed to pull a rope, wire, or a structural beam to the stage where it breaks. Specifically, the tensile strength of a material is the maximum amount of tensile stress that it can withhold before failure occurs. Yield strength, or the yield point, is described in.
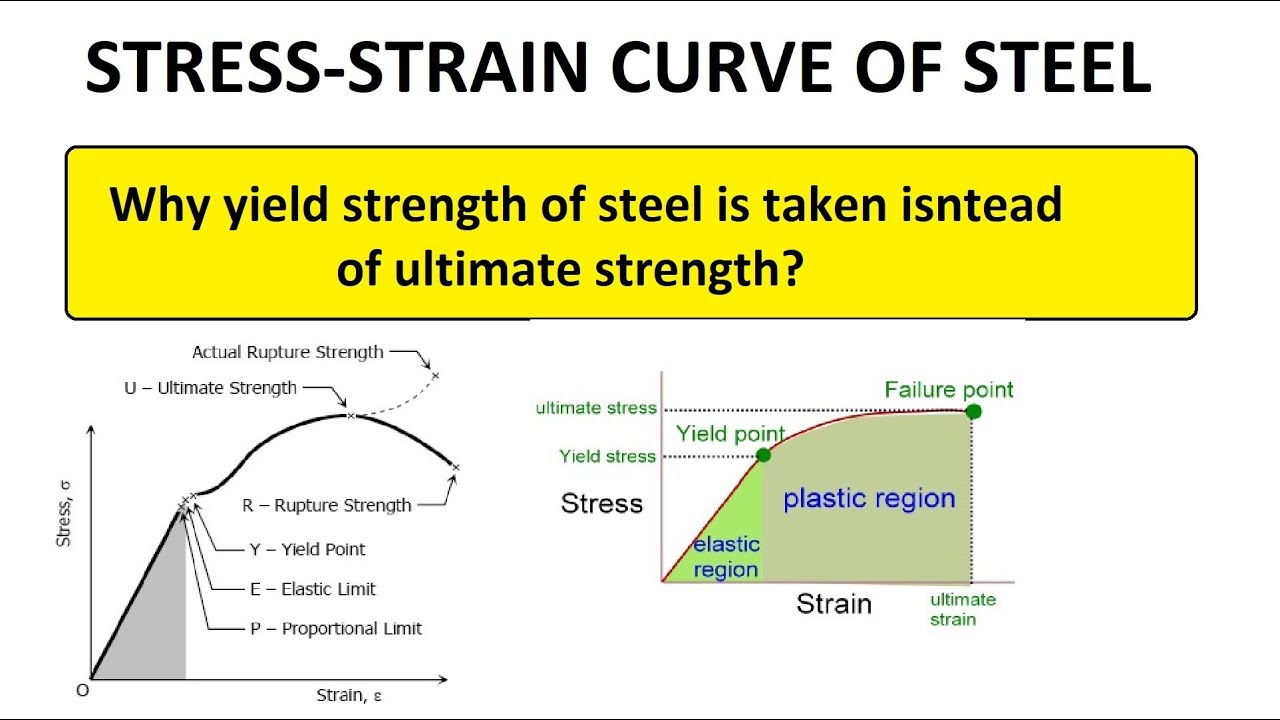
Yield and tensile strength of steel
The main difference between yield strength and tensile strength is that under yield strength, a material changes its form completely, while tensile strength is the stress which a material can handle before it breaks. Let's take a closer look at Tensile Strength vs. Yield Strength Table of Contents What Is Yield Strength?

Yield to tensile strength ratio for different rolling directions Download Scientific Diagram
10. Both yield strength and tensile strength are measures of a material's resistance to mechanical failure, but they signify different behaviors. Yield strength highlights the onset of plastic deformation, while tensile strength signifies the point of outright failure. Sumera Saeed. Oct 04, 2023.
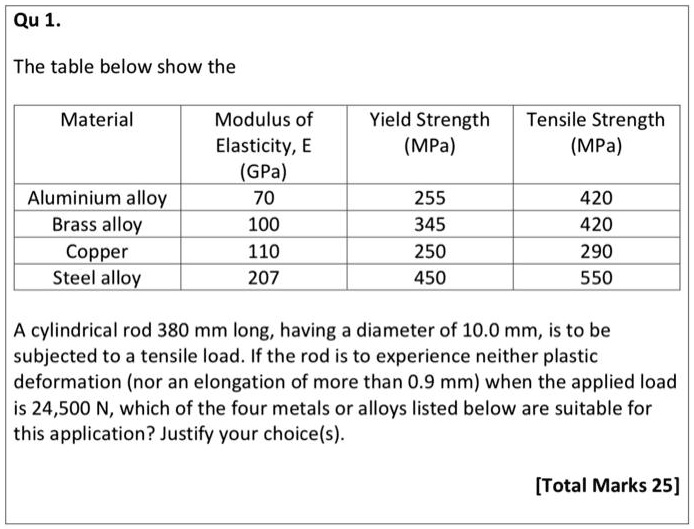
SOLVED Qu 1. The table below show the Yield Strength (MPa) Tensile Strength (MPa) Material
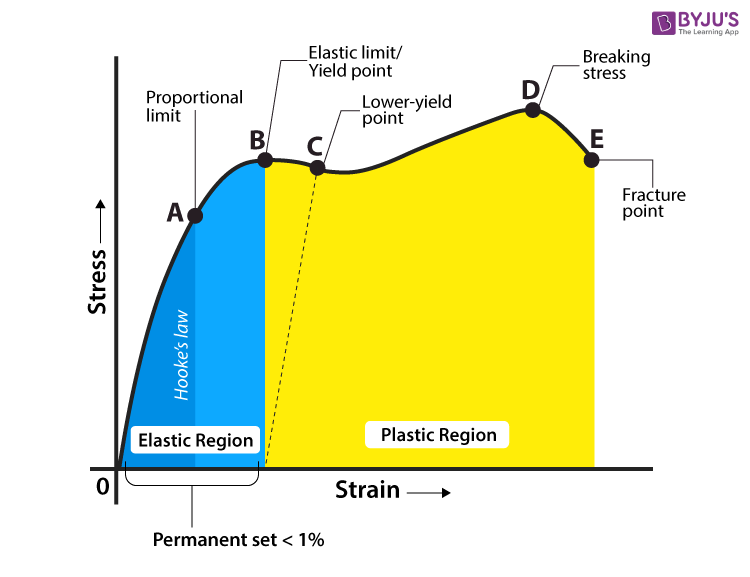
1. Yield Criteria Three commonly used yield criteria in engineering are: (1) Proportional Limit - The highest stress that maintains a linear relationship on the stress-strain curve, internationally represented as σp. Material is considered to start yielding when stress exceeds σp.
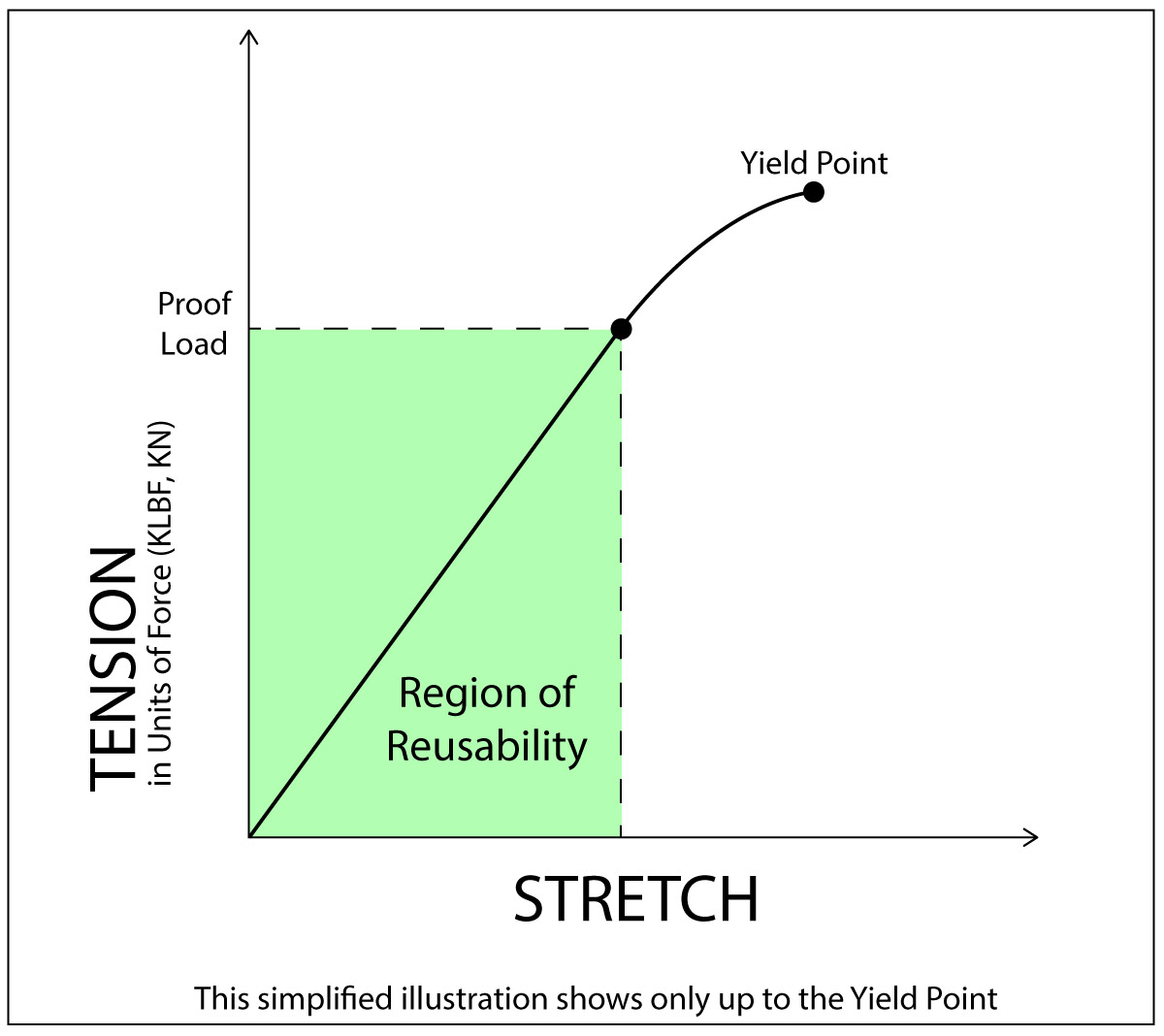
What is Proof Load of a Bolt and How is it Different from Yield Strength? SmartBolts
It can be used to predict the elongation or compression of an object as long as the stress is less than the yield strength of the material. More about the definitions below the table. Young's Modulus, Tensile Strength and Yield Strength Values common Materials 1 Pa (N/m2) = 1x10-6N/mm2= 1.4504x10-4psi

classical mechanics Yield Strength versus Ultimate Strength Physics Stack Exchange
The difference between yield strength and tensile strength is that yield strength is the smallest amount of force that can start the beginning of the deformation of an object. However, tensile strength is just the opposite of that, being the maximum force to cause breakage in an object.
Yield Strength vs. Tensile Strength 6 Key Differences, Pros & Cons, Examples Difference 101
The main difference between yield strength and tensile strength is that yield strength is the minimum stress under which a material deforms permanently, whereas tensile strength describes the maximum stress that a material can handle before breaking. Stress - Strain Characteristics of a Material
Yield Strength Definition, Examples , StressStrain Graph, FAQs
Te nsile Strength The tensile strength is defined as the maximum tensile load a body can withstand before failure divided by its cross sectional area. This property is also sometimes referred to Ultimate Tensile Stress or UTS. Typically, ceramics perform poorly in tension, while metals are quite good.
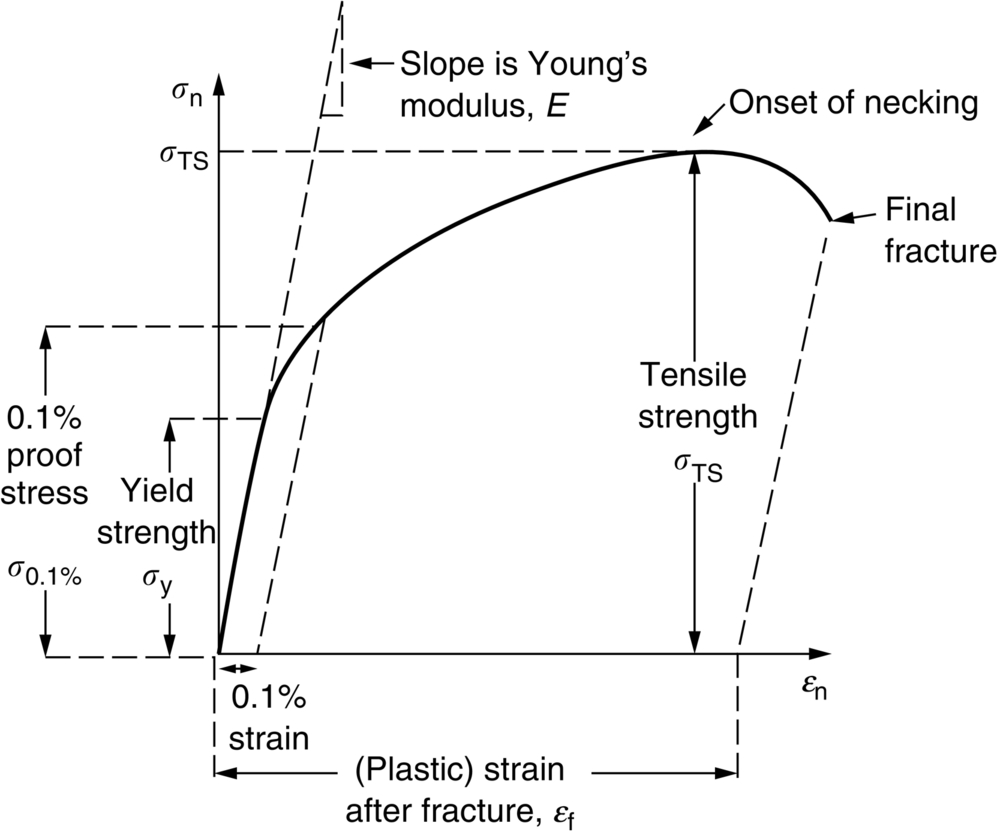
Yield Strength, Tensile Strength, and Ductility Engineer Key
Differences Between Tensile and Yield Strength 1. Definition Tensile Strength: Represents the maximum stress a material can endure while being pulled or stretched. Yield Strength: Indicates the stress at which a material begins to undergo permanent deformation under tension. 2. Behavior Under Load
(a) Yield strength, tensile strength, and Brinell hardness versus... Download Scientific Diagram
In summary, the key difference lies in their definitions and the points on the stress-strain curve at which they are measured. Yield strength is associated with the onset of plastic deformation, while tensile strength is associated with the maximum stress a material can endure before failure. In general, yield strength is used for designing.

Yield Strength Vs Tensile Strength What's The Difference? » Differencess
Key differences between yield and tensile strength These are some of the major differences between yield strength and tensile strength: Yield strength is a measurement to determine the maximum stress that can be applied before permanent shape change is achieved in ductile materials.