How to Use the Sine Rule 11 Steps wikiHow

Law of Sine, Laws and Formulas, Properties of Trigonometric Functions 24/12 Sideway output.to
The basic relationship between the sine and cosine is given by the Pythagorean identity: where means and means This can be viewed as a version of the Pythagorean theorem, and follows from the equation for the unit circle.

sin ( AB ) = sin A cos B cosA sinB proof Trigonometry By J.P. Verma YouTube
The Law of Sines The Law of Sines (or Sine Rule) is very useful for solving triangles: a sin A = b sin B = c sin C It works for any triangle: And it says that: When we divide side a by the sine of angle A it is equal to side b divided by the sine of angle B, and also equal to side c divided by the sine of angle C Sure. ?

An Alternative Sine Rule Proof a/sinA = b/sinB = c/sinC YouTube
Part of Maths Geometry and measure The sine rule - Higher The angles are labelled with capital letters. The opposite sides are labelled with lower case letters. Notice that an angle and its.

Simple But Elegant Way To Prove That sin(A+B)=sinAcosB+cosAsinB (Edexcel Proof Simplified
In this post, we will establish the formula of sin (a+b) sin (a-b). Note that sin (a+b) sin (a-b) is a product of two sine functions. We will use the following two formulas: sin (a+b) = sin a cos b + cos a sin b. (i) sin (a-b) = sin a cos b - cos a sin b. (ii) Table of Contents Formula of sin (a+b) sin (a-b) sin (a+b) sin (a-b) Formula:

7 TRIGONOMETRY ( PRODUCT FORMULA SIN(A+B).SIN(AB),COS ALSO AND SOME IMPORTANT TRICK) YouTube
Sin (A + B) is the two parts of the opposite - all divided by the hypotenuse (9). Putting that into its trig form: sin (A + B) = sin A cos B + cos A sin B

Visual proof of sin(A+B) formula YouTube
Sin (a + b) is one of the important trigonometric identities used in trigonometry. It is one of sum and difference formulas. It says sin (a + b) = sin a cos b + cos a sin b. We use the sin (a + b) identity to find the value of the sine trigonometric function for the sum of angles.

Trigonometric Addition and Difference Formulas (Identities) Also double angle formulas. hubpages
Sin (a - b) is one of the important trigonometric identities used in trigonometry, also called sin (a - b) compound angle formula. Sin (a - b) identity is used in finding the value of the sine trigonometric function for the difference of given angles, say 'a' and 'b'.
Expert Maths Tutoring in the UK Boost Your Scores with Cuemath
Sin A - Sin B is an important trigonometric identity in trigonometry. It is used to find the difference of values of sine function for angles A and B. It is one of the difference to product formulas used to represent the difference of sine function for angles A and B into their product form.

How to Use the Sine Rule 11 Steps wikiHow
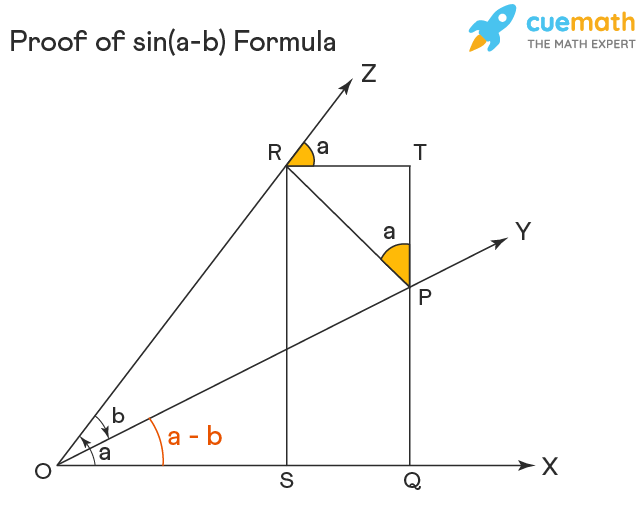
Mathematical form The sine of difference of two angles formula can be written in several ways, for example sin ( A − B), sin ( x − y), sin ( α − β), and so on but it is popularly written in the following three mathematical forms. ( 1) sin ( A − B) = sin A cos B − cos A sin B ( 2) sin ( x − y) = sin x cos y − cos x sin y

pembuktian sin A+sin B=2 sin (A+B/2) cos (AB/2) Trigonometry Explanation eps. 42 how to
The following (particularly the first of the three below) are called "Pythagorean" identities. sin 2 ( t) + cos 2 ( t) = 1. tan 2 ( t) + 1 = sec 2 ( t) 1 + cot 2 ( t) = csc 2 ( t) Advertisement. Note that the three identities above all involve squaring and the number 1. You can see the Pythagorean-Thereom relationship clearly if you consider.
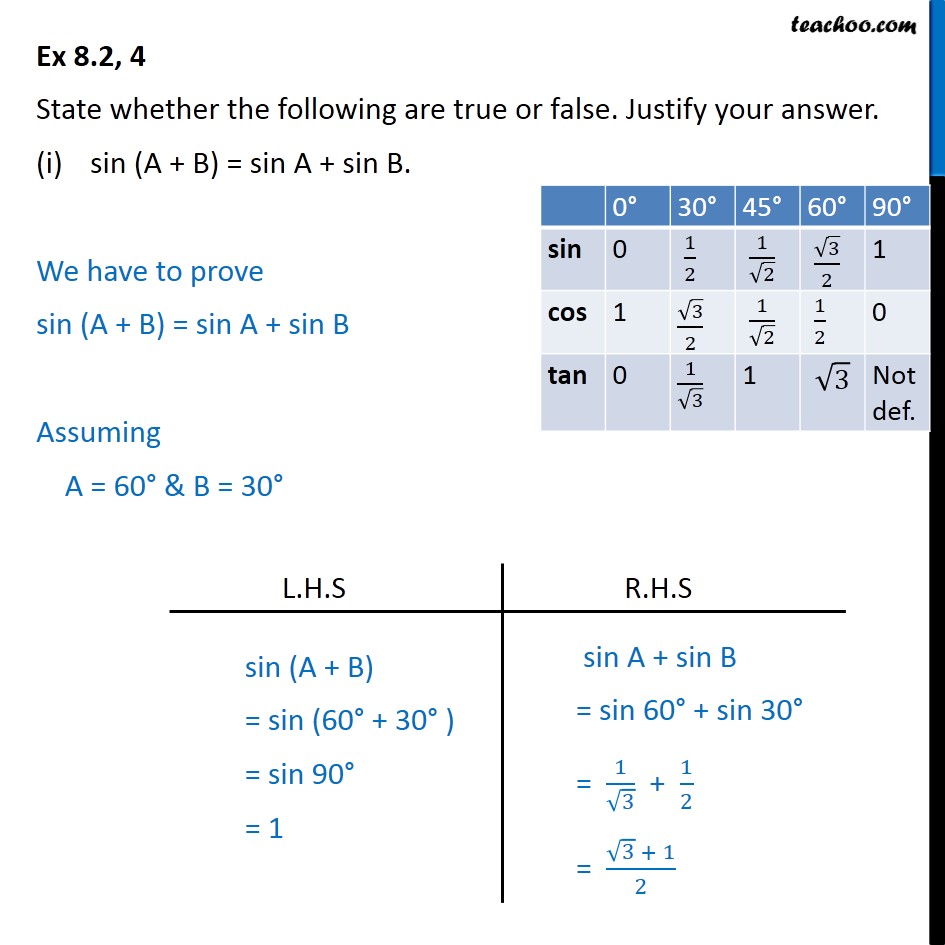
Ex 8.2, 4 (i) Class 10 State True or False sin (A + B) = sin A
Trigonometric Identities are the equalities that involve trigonometry functions and holds true for all the values of variables given in the equation. There are various distinct trigonometric identities involving the side length as well as the angle of a triangle. The trigonometric identities hold true only for the right-angle triangle.

How to prove by vector method Sin(AB)= SinA CosBCosA SinB ? Math Village
Free trigonometry calculator - calculate trignometric equations, prove identities and evaluate functions step-by-step

proof of sin(a+b) identity YouTube
3/1. 4/0. Given Triangle abc, with angles A,B,C; a is opposite to A, b opposite B, c opposite C: a/sin (A) = b/sin (B) = c/sin (C) (Law of Sines) c ^2 = a ^2 + b ^2 - 2ab cos (C) b ^2 = a ^2 + c ^2 - 2ac cos (B) a ^2 = b ^2 + c ^2 - 2bc cos (A) (Law of Cosines)

Identities for Sin(A + B) and Sin(A B) YouTube
1 4 involving products of sines and cosines now add equation (2) to equation (7) sin(A − B) +(sin(A + B) = sin A cos B − cos A sin B = sin A cos B + cos A sin B) we find sin(A − B) + sin(A + B) = 2 sin A cos B and dividing both sides by 2 we obtain the identity 1 1 sin A cos B = sin(A − B) + sin(A + B). 2 2

Даю 50 баллов!!!! Помоги Алгебра.упростите выраженияsin (aB) + 2 cos a×sin B Школьные
The sin A + sin B sum to product formula in trigonometry for angles A and B is given as, Sin A + Sin B = 2 sin [½ (A + B)] cos [½ (A - B)] Here, A and B are angles, and (A + B) and (A - B) are their compound angles. Proof of SinA + SinB Formula
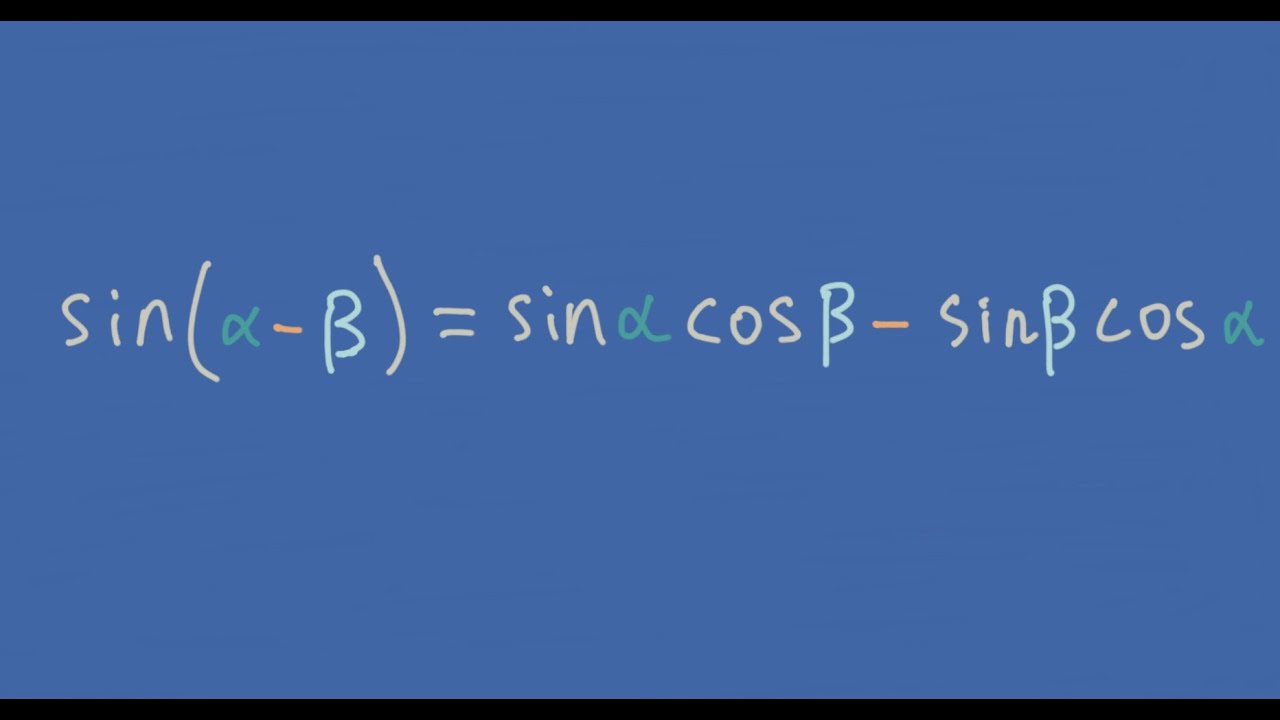
sin(ab) Formula DERIVED YouTube
The six trigonometric functions are sine, cosine, secant, cosecant, tangent and cotangent. By using a right-angled triangle as a reference, the trigonometric functions and identities are derived: sin θ = Opposite Side/Hypotenuse. cos θ = Adjacent Side/Hypotenuse. tan θ = Opposite Side/Adjacent Side.