The left recurrent laryngeal nerve is a branch of the vagus nerve,... Download Scientific Diagram
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/recurrent-laryngeal-nerve/X47SfEepDTCmvKgFKsk4eQ_Nervus_laryngeus_recurrens_02.png)
Pharyngeal arches Anatomy and clinical aspects Kenhub
Poster: "ECR 2019 / C-2121 / Nervus laryngeus recurrens anatomy and pathology" by: " V. Pesti ; Budapest/HU" Poster: "ECR 2019 / C-2121 / Nervus laryngeus recurrens anatomy and pathology " by: " V.. If other cranial nerve involvement suggests high-vagal injury, MRI is preferable. Foremost, the radiologist ought to search for a malignant mass.
Genes Free FullText Gene Therapy for Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Injury
Discover the anatomy of the recurrent laryngeal nerve, its origin, course, branches, and functions in sensory and motor supply. Learn about related clinical correlates. Skip to main content.. Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve . Nervus laryngeus recurrens Read more. Quick Facts. Origin.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/nervus-laryngeus-recurrens-dexter-2/VC2BeBcj6MuuSannA1UQ_N._laryngeus_recurrens_dexter_01.png)
Faringe Anatomia, músculos, artérias e nervos Kenhub
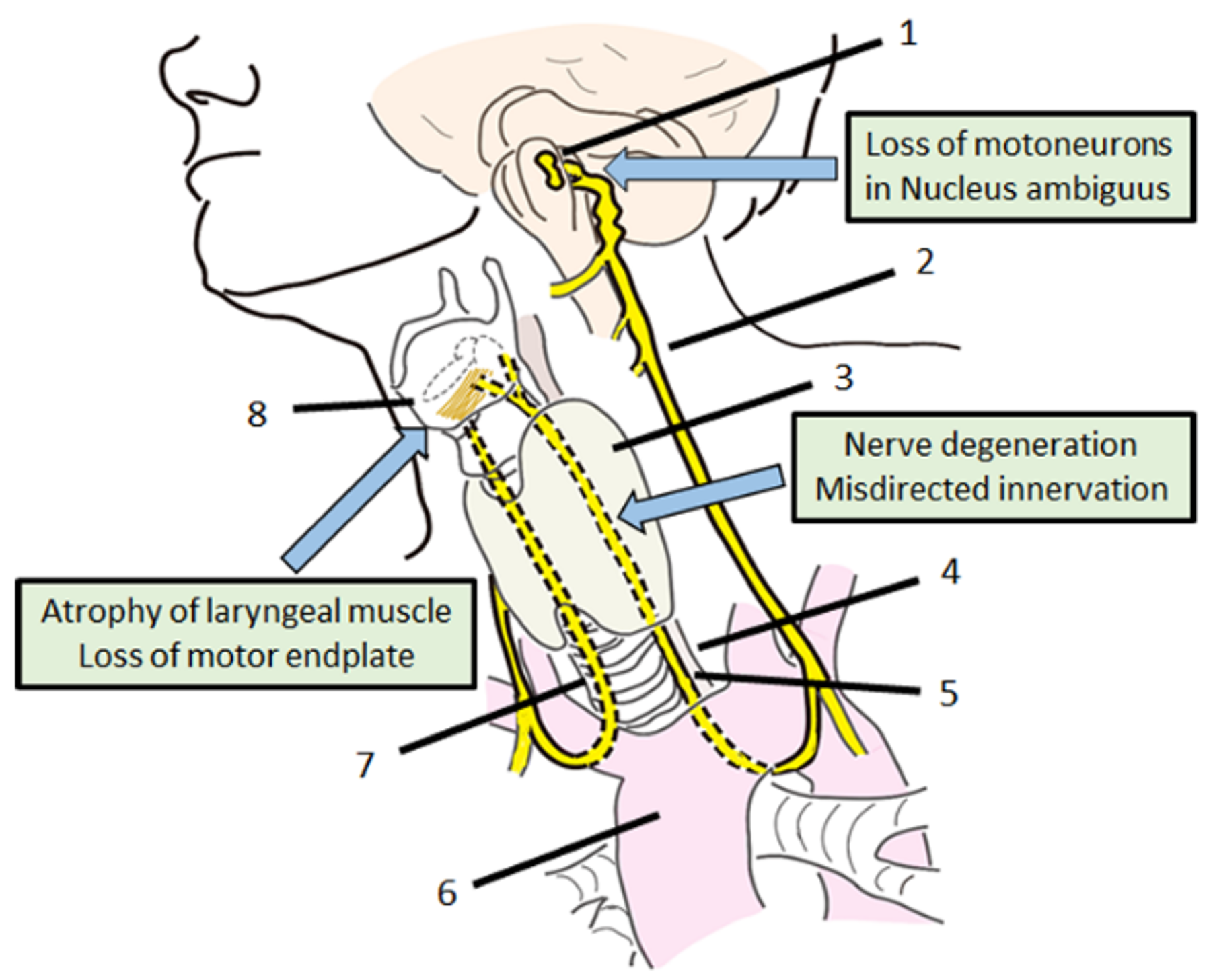
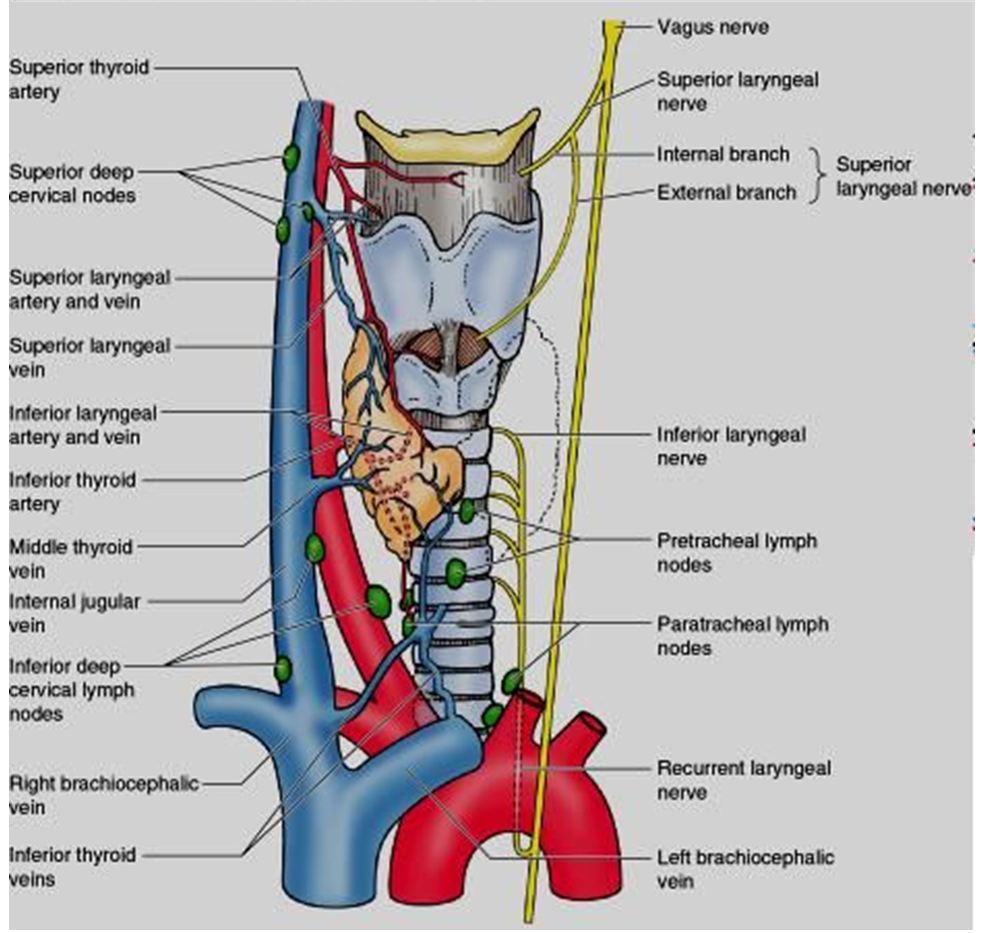
The recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) branches off the vagus nerve (cranial nerve X) and has an indirect course through the neck. It supplies innervation to all of the intrinsic muscles of the larynx, except for the cricothyroid muscles, as well as sensation to the larynx below the level of the vocal cords. The right RLN branches from CN X around the level of T1-T2 loops under the right.
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/nervus-laryngeus-recurrens-dexter/3TlZtPA2mDjNirkzl11luw_Nervus_laryngeus_recurrens_dexter_01.png)
Nervus Laryngeus Recurrens Anatomie Verlauf Klinik Kenhub My XXX Hot Girl
The recurrent laryngeal nerves (RLN) are branches of the vagus nerve that go on to innervate most of the intrinsic muscles of the larynx. Historically, the RLN has been considered to branch after it enters the larynx, but numerous studies have demonstrated that it often branches before. The wide variability of this extralaryngeal branching (ELB.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/nervus-laryngeus-recurrens/tV5udWXGgWcB9YRBZxJkIQ_Nervus_laryngeus_recurrens_01.png)
Nervus laryngeus recurrens Anatomie, Verlauf & Klinik Kenhub
Nervus laryngeus recurrens 1/4. Synonyms: none. Function. Action of vocalis and thyroarytenoid muscles Functio musculorum vocalis et thyroarytenoidei Synonyms: Protrusion of arytenoid cartilage, Protrusio cartilaginis arytenoideae The vocalis muscle makes small adjustments to the tension of the vocal ligaments. Similar to a rubber band.

Course and branches of recurrent laryngeal nerves (RLN) and superior... Download Scientific
The recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) is critical for speech as it provides nerve function to muscles in the larynx, or voice box. People have two RLNs, one on each side of the neck. Instead of.

The left recurrent laryngeal nerve is a branch of the vagus nerve,... Download Scientific Diagram
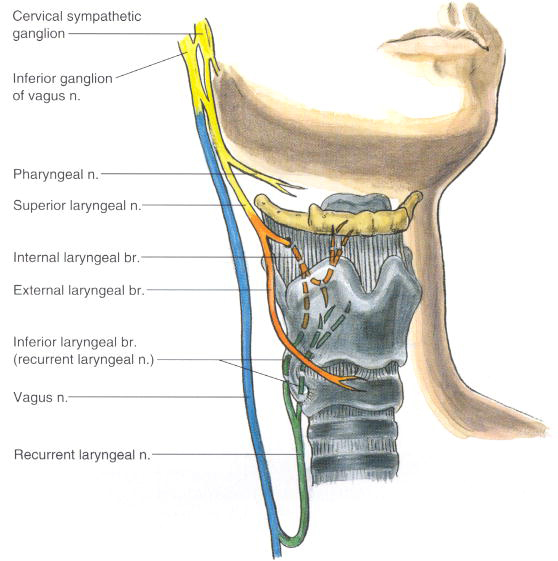
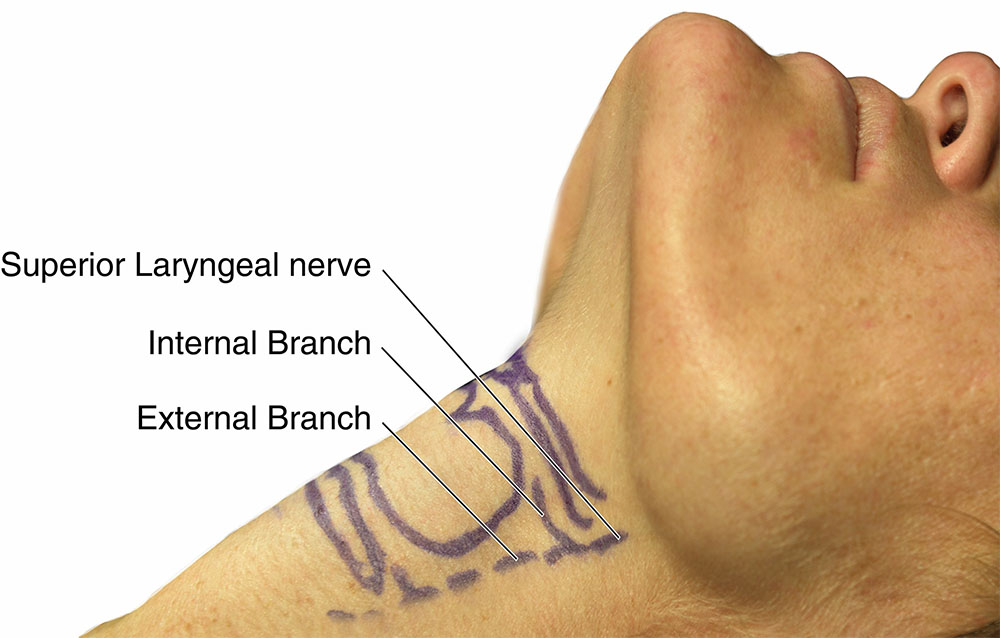
Synonyms: Nervus laryngeus cranialis It is a structure of IV branchial arch and thus innervates the pharyngeal and laryngeal derivatives of this arch. The afferent fibers of the superior laryngeal nerve arise from the inferior ganglion of the vagus nerve.. Nervus laryngeus recurrens 1/3.
závraty uskutočniteľnosť vysvetliť nervus laryngeus recurrens nervove pero miešačka Prepáč
Poster: "ECR 2019 / C-2121 / Nervus laryngeus recurrens anatomy and pathology " by: " V. Pesti ; Budapest/HU" Brought to you by. Browse Posters » Search result » Poster ECR 2019 / C-2121 POSTER SECTIONS Coverpage Learning objectives Background Findings and procedure details Conclusion Personal information References. ECR 2019 / C-2121.
Anatomía de la laringe
Nervus laryngeus recurrens 1/3. Synonyms: none. Function. Action of lateral cricoarytenoid muscle Functio musculi cricoarytenoidei lateralis 1/2. Synonyms: Adduction of vocal folds, Adductio plicae vocalis The intrinsic laryngeal muscles, of which the lateral cricoarytenoid is a part, are all involved in the production of sound (phonation).

Recurrent laryngeal nerve anatomy Vagus nerve, Nerve anatomy, Medical
Nervus laryngeus recurrens 1/5. Synonyms: none. Function. Action of vocalis and thyroarytenoid muscles. Due to its complex structure and multiple points of attachment, the thyroarytenoids aid in two distinct actions simultaneously; they draw the arytenoid cartilages anteriorly allowing the vocal ligaments to shorten, thicken and relax.

Nervus Laryngeus Recurrens Human Anatomy Human Head And Neck
nervus laryngeus superior: TA98: A14.2.01.160: TA2: 6339: FMA: 6239: Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy [edit on Wikidata] The superior laryngeal nerve is a branch of the vagus nerve. It arises from the middle of the inferior ganglion of vagus nerve and additionally also receives a sympathetic branch from the superior cervical ganglion.
The Recurrent Laryngeal Nerves and the Thoracic Surgeon
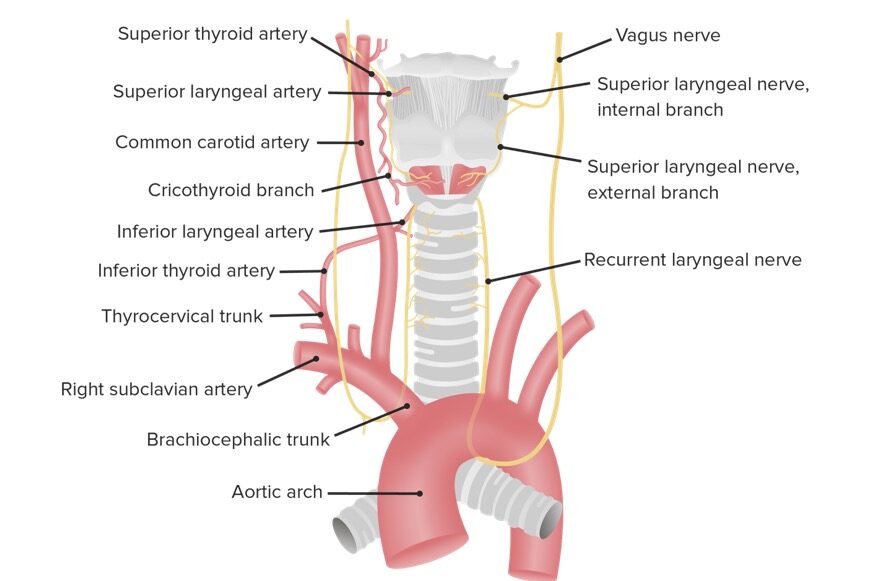
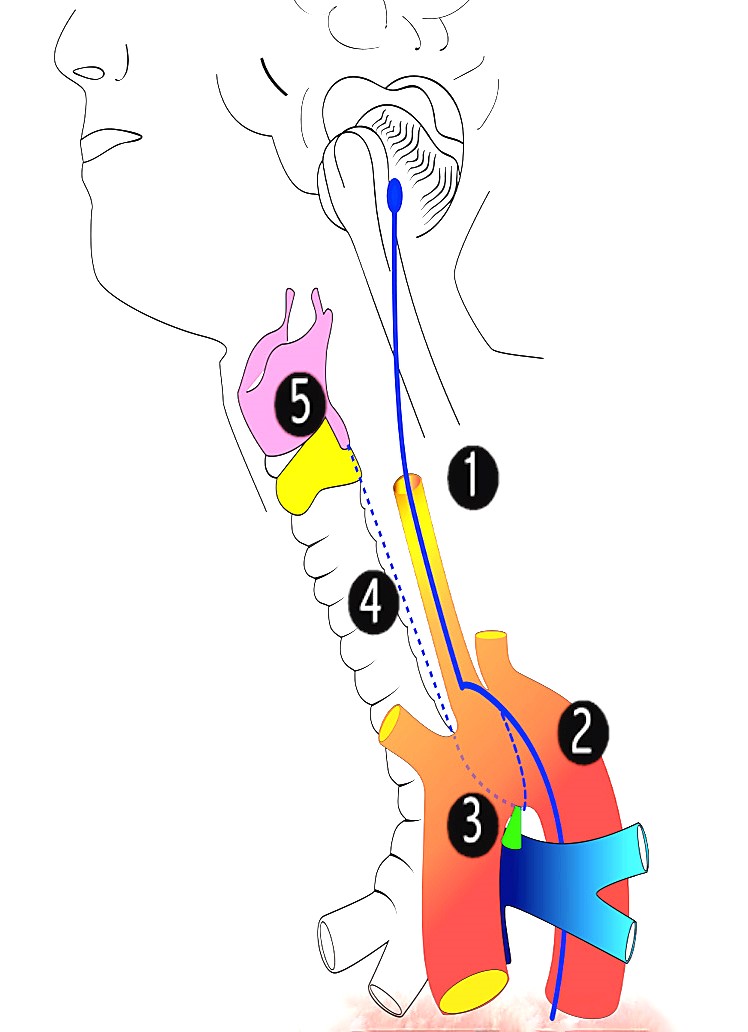
The Recurrent Nerve (n. recurrens; inferior or recurrent laryngeal nerve) arises, on the right side, in front of the subclavian artery; winds from before backward around that vessel, and ascends obliquely to the side of the trachea behind the common carotid artery, and either in front of or behind the inferior thyroid artery. On the left side, it arises on the left of the arch of the aorta.

Recurrent laryngeal nerve Wikipedia
Nervus laryngeus recurrens 1/4.. The transverse arytenoid muscle also receives branches from the internal branches of the superior laryngeal nerve, another branch of the vagus nerve. However there is debate about whether these nerves provide any motor innervation, as the internal branch is considered to only contain sensory fibres..
Laryngeal Manifestations of Rheumatoid Arthritis IntechOpen
nervus laryngeus recurrens: MeSH: D012009: TA98: A14.2.01.166: TA2: 6344: FMA: 6246: Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy [edit on Wikidata] The recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) is a branch of the vagus nerve (cranial nerve X) that supplies all the intrinsic muscles of the larynx, with the exception of the cricothyroid muscles. There are two.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/musculus-cricoarytaenoideus-lateralis/uDGo8KuhYbwE24w02LADQ_Musculus_cricoarytaenoideus_lateralis_01.png)
Nervus laryngeus recurrens Anatomie, Verlauf & Klinik Kenhub
The recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) branches off the vagus nerve (cranial nerve X) and has an indirect course through the neck. It supplies innervation to all of the intrinsic muscles of the larynx, except for the cricothyroid muscles, as well as sensation to the larynx below the level of the vocal cords. The right RLN branches from CN X around.
Nervus laryngeus recurrens kreacionismus.cz
The Greek physician, Galen of Pergamon (129-210) was the first to describe the recurrent laryngeal nerve as a branch of a cranial nerve and famously demonstrated its role in vocalization when he accidentally cut the recurrent laryngeal nerve of a squealing pig 4 . The word recurrent is derived from the Latin word "recurrere" meaning "to run.