Eukaryotic Cell Definition, Structure, & Examples

Eukaryotic Cell Definition, Characteristics, Structure and Examples
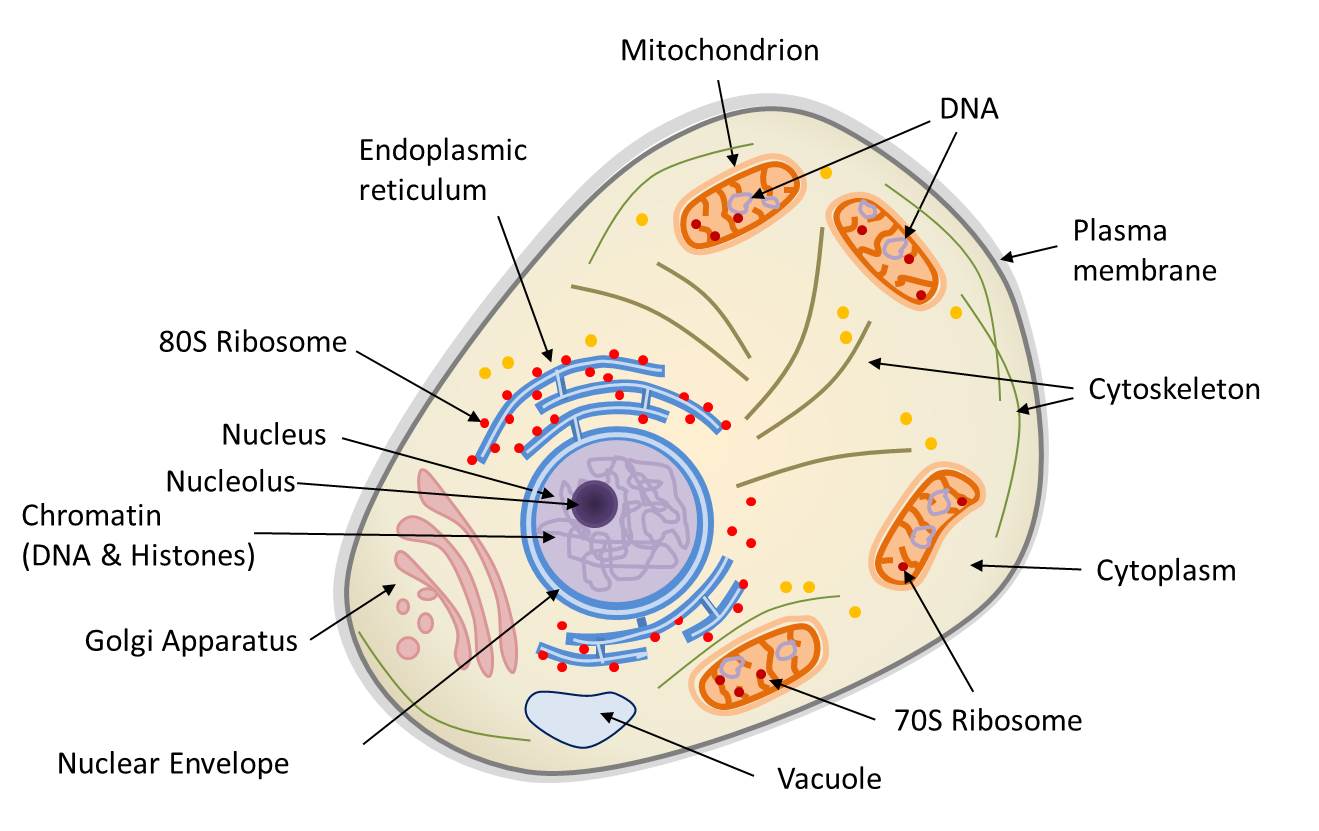
Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: 1) a membrane-bound nucleus; 2) numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others; and 3) several, rod-shaped chromosomes. Because a membrane surrounds eukaryotic cell's nucleus, it has a "true nucleus.".
Symbiosis and evolution at the origin of the eukaryotic cell
There are two general classes of cells that exist: the self-sustaining simple cells known as prokaryotic (bacteria and archaea) and the more complex dependent cells known as eukaryotic. The eukaryotic cells types are generally found in animals, plants, algae, and fungi.
Eukaryotic Cells Definition, Characteristics, Structure, & Examples
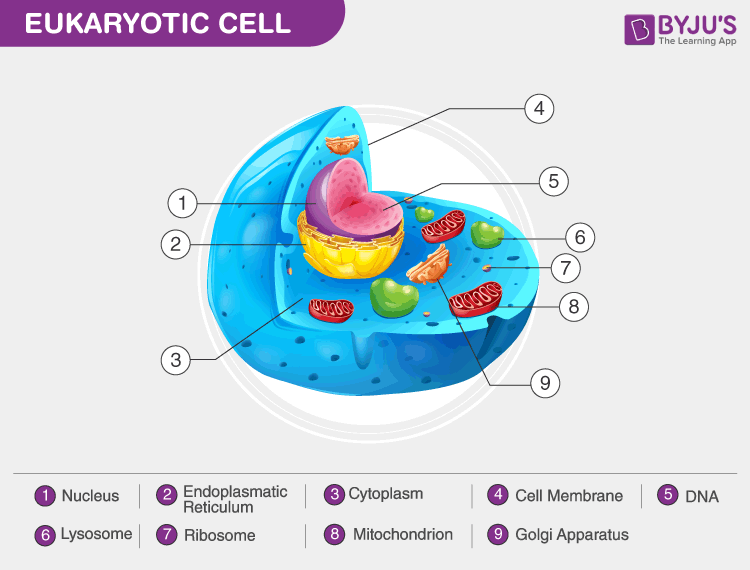
Definition A eukaryotic cell contains membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus, mitochondria, and an endoplasmic reticulum. Organisms based on the eukaryotic cell include protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals. These organisms are grouped into the biological domain Eukaryota.
Biology Club Our cells 1 ( structure, function, division, disorder
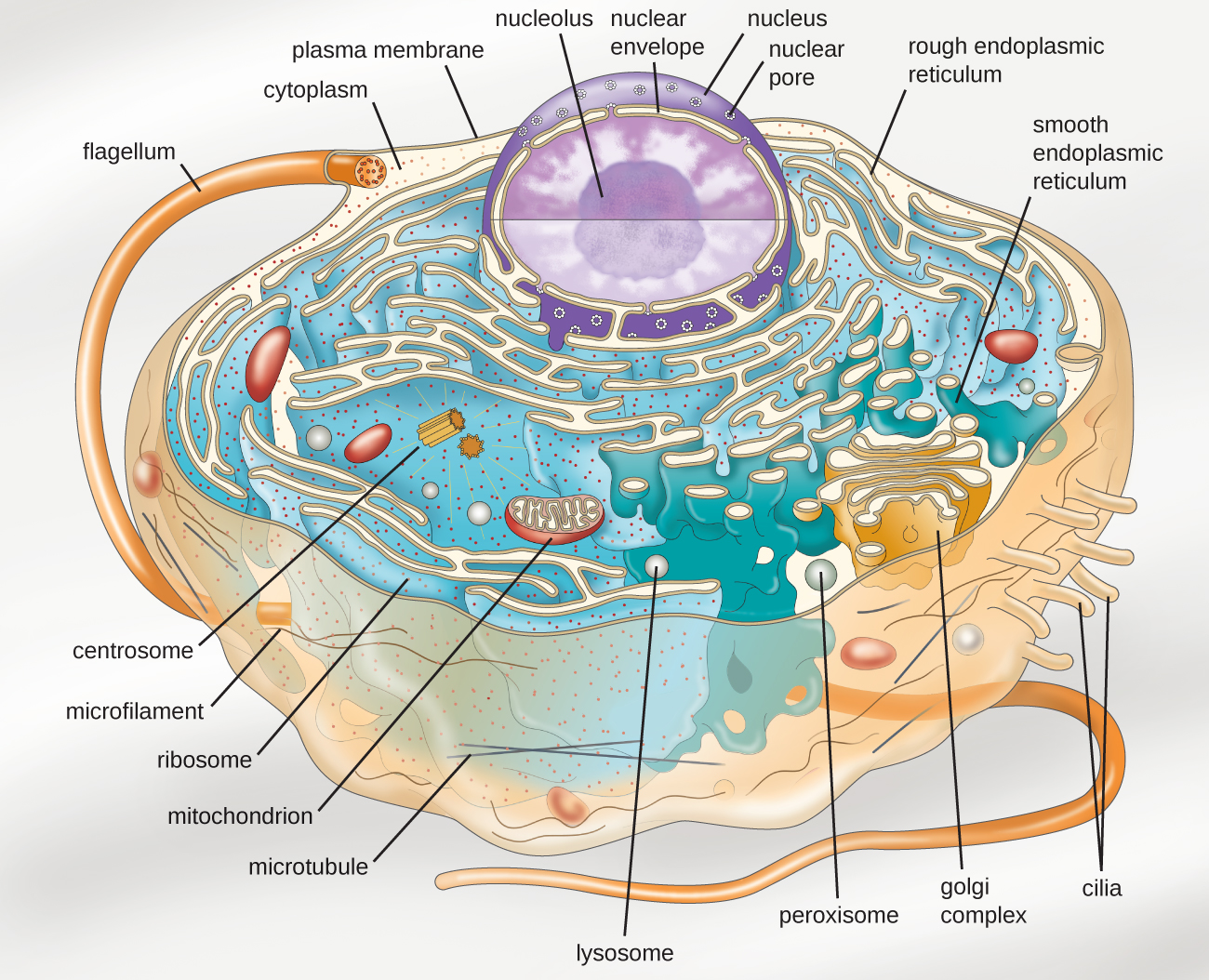
In Figure 1b, the diagram of a plant cell, you see a structure external to the plasma membrane called the cell wall. The cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell.. Like a prokaryotic cell, a eukaryotic cell has a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and ribosomes, but a eukaryotic.

Eukaryotic cell structure diagrams Biological Science Picture
The Cell Wall. In Figure 3.3. 1 b, the diagram of a plant cell, you see a structure external to the plasma membrane called the cell wall. The cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. Fungal and protist cells also have cell walls.

Eukaryotic Cell
What are the key features of eukaryotic cells? Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: A membrane-bound nucleus, a central cavity surrounded by membrane that houses the cell's genetic material. A number of membrane-bound organelles, compartments with specialized functions that float in the cytosol.
3.4 Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells Microbiology 201
Diagram Cell Cycle Examples What is a Eukaryotic Cell? Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane and form large and complex organisms. Protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals all have eukaryotic cells. They are classified under the kingdom Eukaryota.
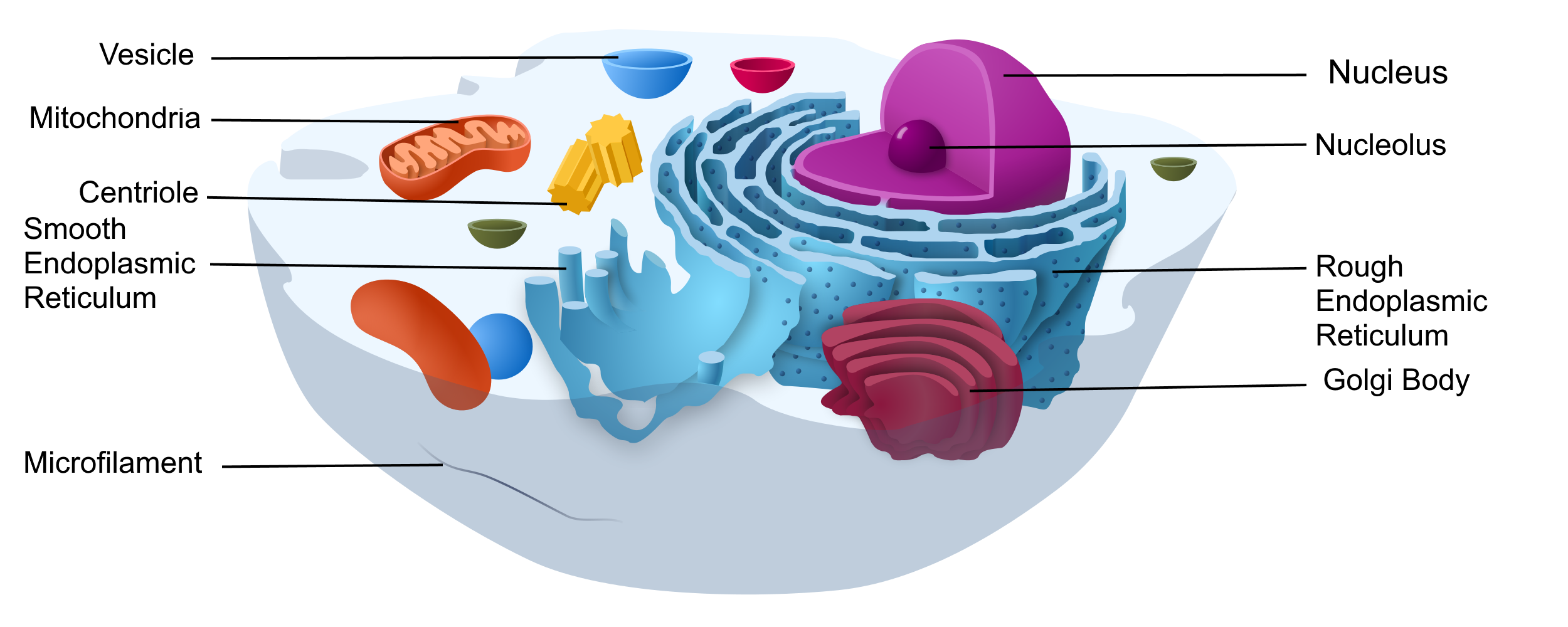
4.3 Variation in Cells Human Biology
Figure 4.7.1 4.7. 1: Eukaryotic Plasma Membrane: The eukaryotic plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with proteins and cholesterol embedded in it. The cell membrane is an extremely pliable structure composed primarily of two adjacent sheets of phospholipids. Cholesterol, also present, contributes to the fluidity of the membrane.
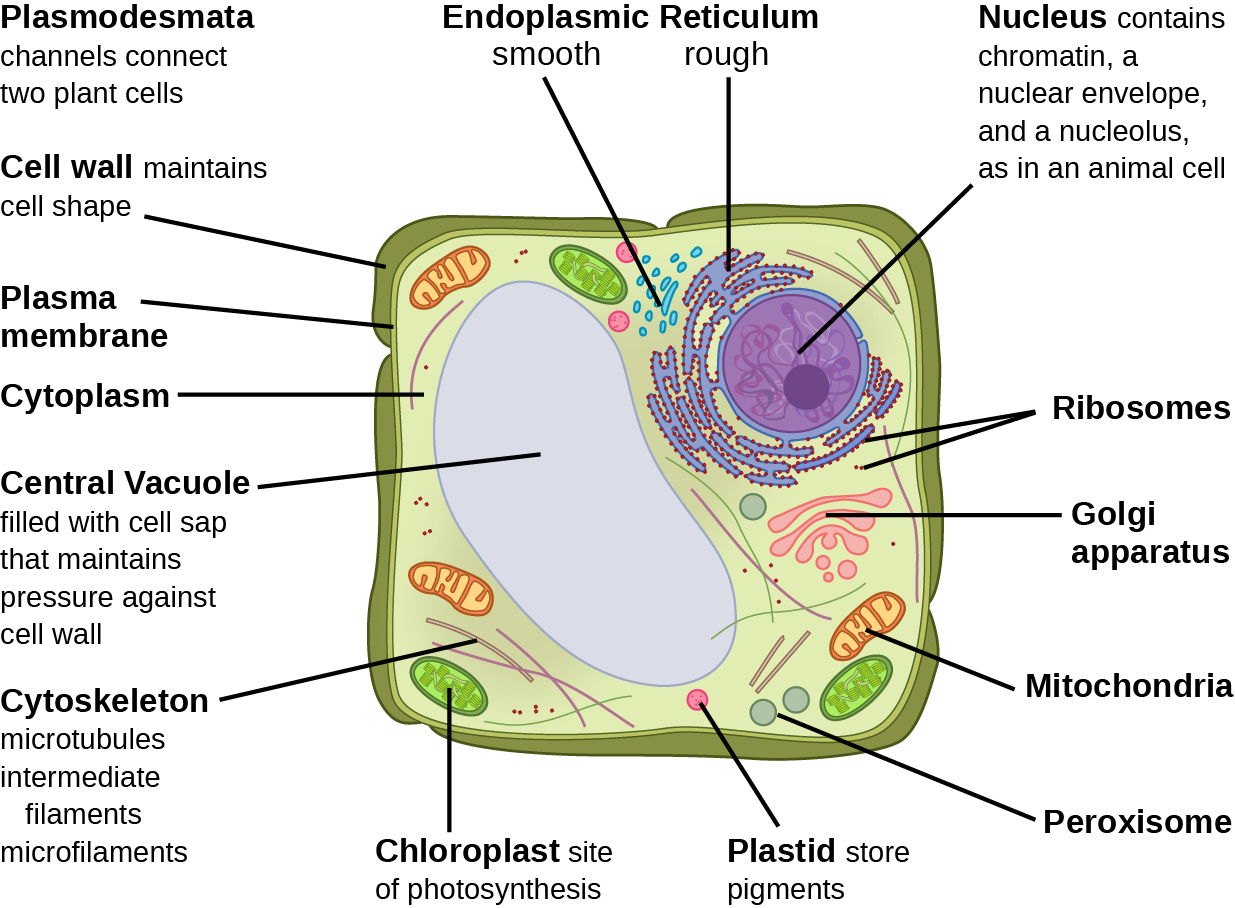
Biology 2e, The Cell, Cell Structure, Eukaryotic Cells OpenEd CUNY
Eukaryotes are organisms that contain a nucleus, organelles, and membrane-bound cytoplasm enclosed by a cell membrane. Eukaryotic cells are the vast majority of all life forms on Earth and are the basis for all known life. The structure and functions of a eukaryotic cell are unique. Eukaryotic cells have a mitochondrial genome.

Characteristics Of Eukaryotic Cellular Structures ALevel Biology
Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: 1) a membrane-bound nucleus; 2) numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others; and 3) several, rod-shaped chromosomes. Because a membrane surrounds eukaryotic cell's nucleus, it has a "true nucleus."

1.4. Eucaryotic cell structure Biolulia European Sections
A eukaryotic cell cycle is an ordered event involving cell growth and division, producing two daughter cells through mitosis. The cell cycle length is highly variable within the different cell types. An early embryonic cell has a turnover range of a few hours. For epithelial cells in humans, it is about two to five days.

Biology 2e, The Cell, Cell Structure, Eukaryotic Cells OpenEd CUNY
A eukaryotic cell is a type of cell characterized by a membrane-bound nucleus and the presence of various organelles within its cytoplasm, distinguishing it from prokaryotic cells which lack a true nucleus. Eukaryotic cells are found in organisms such as plants, animals, fungi, and many unicellular entities.

Eukaryotic Cell The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
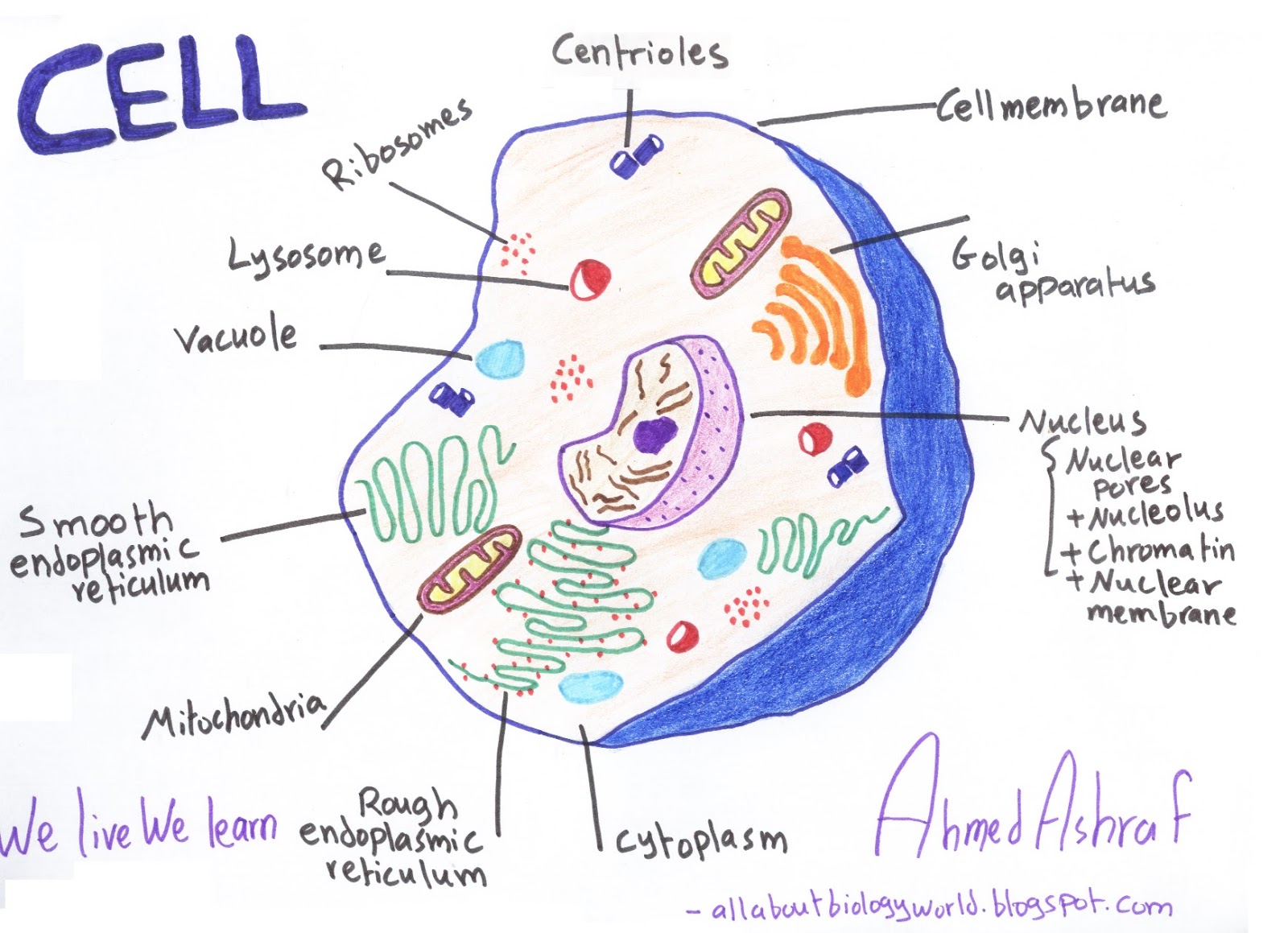
Eukaryotic cells also contain organelles, including mitochondria (cellular energy exchangers), a Golgi apparatus (secretory device), an endoplasmic reticulum (a canal-like system of membranes within the cell), and lysosomes (digestive apparatus within many cell types).
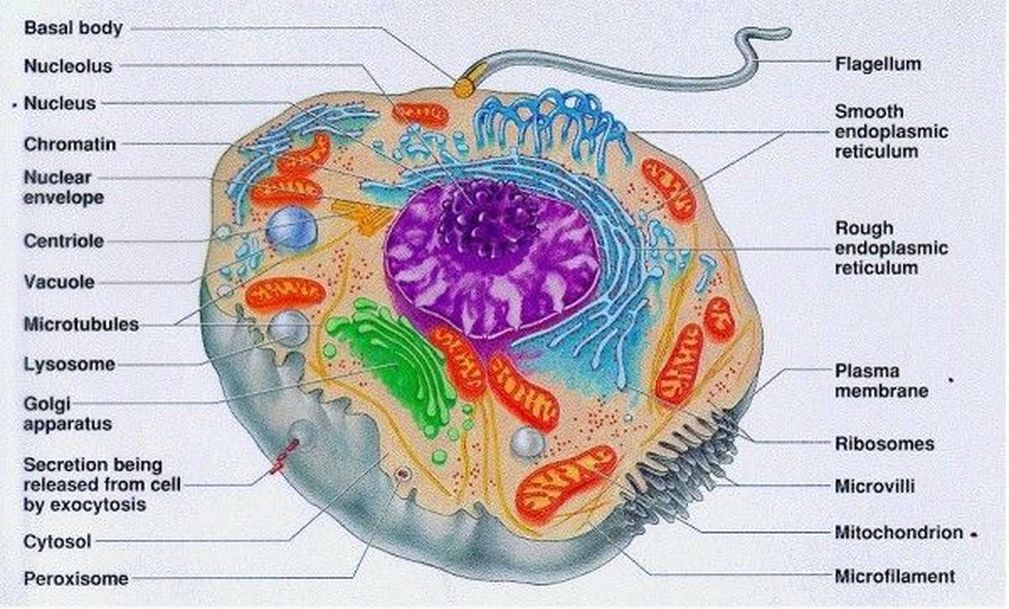
2.4 Eukaryotic Cell Structure a level biology student
Eukaryotic cell: Prokaryotic cell: Size: Most are 5 μm - 100 μm: Most are 0.2 μm - 2.0 μm: Outer layers of cell: Cell membrane - surrounded by cell wall in plants and fungi

Biology 101 Cells Owlcation
By definition, eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus, a structural feature that is not present in bacterial or archaeal cells. In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells are characterized by numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others.
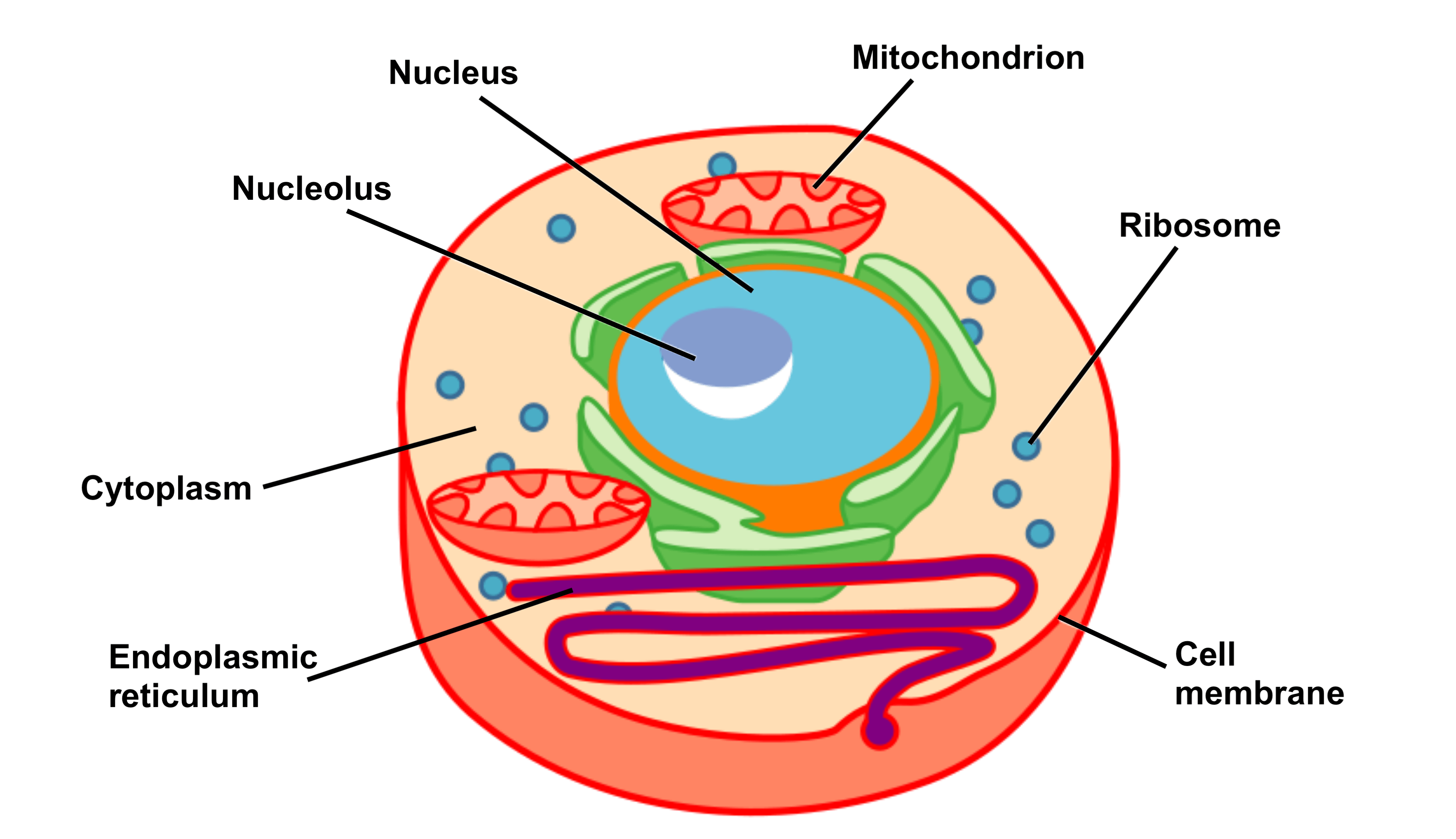
Cell Structure and Function Part 1 The Organelles Medical Exam Prep
An organelle (think of it as a cell's internal organ) is a membrane bound structure found within a cell. Just like cells have membranes to hold everything in, these mini-organs are also bound in a double layer of phospholipids to insulate their little compartments within the larger cells.