Dativ Pronomen Personalpronomen Dativ Und Akkusativ Und Dativ Verben

Prognose Stout Widmung akkusativ dativ und nominativ ara Nicht
The Basics - Nominativ, Akkusativ oder Dativ? (Oder Genitiv?) To be able to follow this step-by-step guide you should have gone through all of the following topics already: The 4 German Cases (Nominative, Accusative, Dative und Genitive) Prepositions; Verbs with Complements; This guide is a summary of all the rules in a way that is easy to put.

de a gestiona Concluzie scris der die das dativ und akkusativ Roti
The nominative case, which focuses on the subject of a sentence The accusative case, which deals with the direct object The dative case, which highlights the indirect object The genitive case, which shows possession and other relationships We'll discover the prepositions that work with these cases.
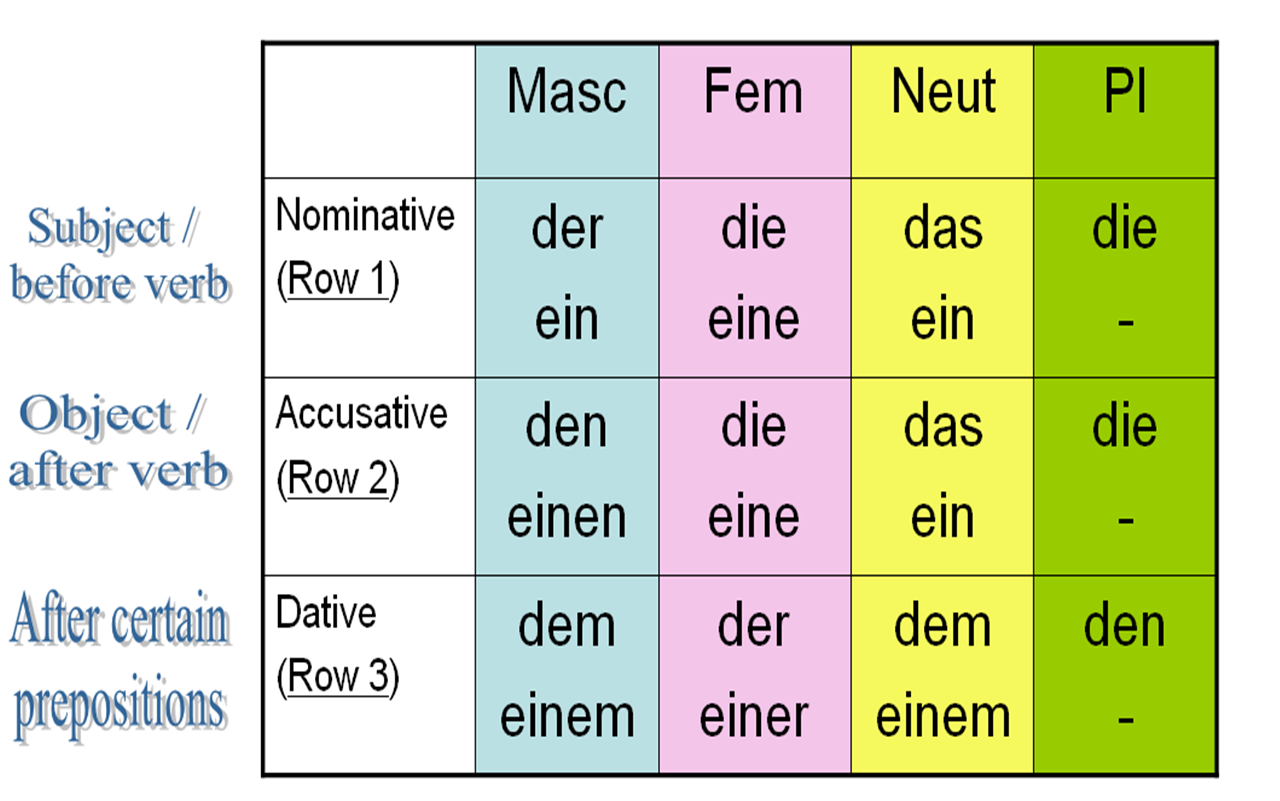
Schöne Gedanken Nominativ , Akkusativ , Dativ
The four German cases are nominative, accusative, dative, and genitive. The nominative case is used for sentence subjects. The subject is the person or thing that does the action. For example, in the sentence, "the girl kicks the ball", "the girl" is the subject. The accusative case is for direct objects.

Nominativ, Akkusativ und Dativ Deutsch Viel Spass
Grammar Nominative and accusative Summary: Nominative and accusative within a sentence Nominative The subject of a sentence is always in the nominative case. Der Mann sucht seinen.

Nominativ / Akkusativ / Dativ Deutsch DAF Arbeitsblätter pdf & doc
German has "only" 4 cases: Nominative (Nominativ) Accusative (Akkusativ) Dative (Dativ) Genitive (Genitiv) Other languages have a way more! Hungarian: 18 cases. Finish: 15 cases. So take it positive and appreciate that you only have to learn four cases.
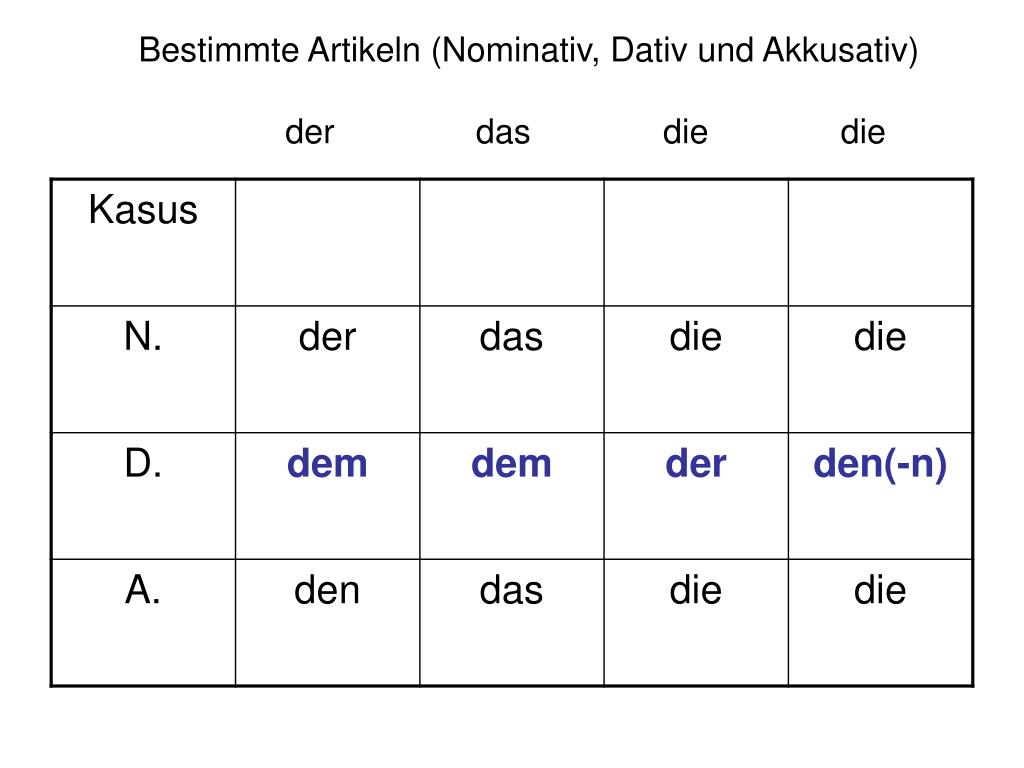
Die In Akkusativ Nehru Memorial
In short, the nominative case is used to refer to who is doing the action, and the accusative case is used to refer to who is having the action done to them. In this article, I'll quickly break down the nominative vs accusative German cases, and give you an easy summary of how to use them. Contents What Are Grammatical Cases, Anyways?
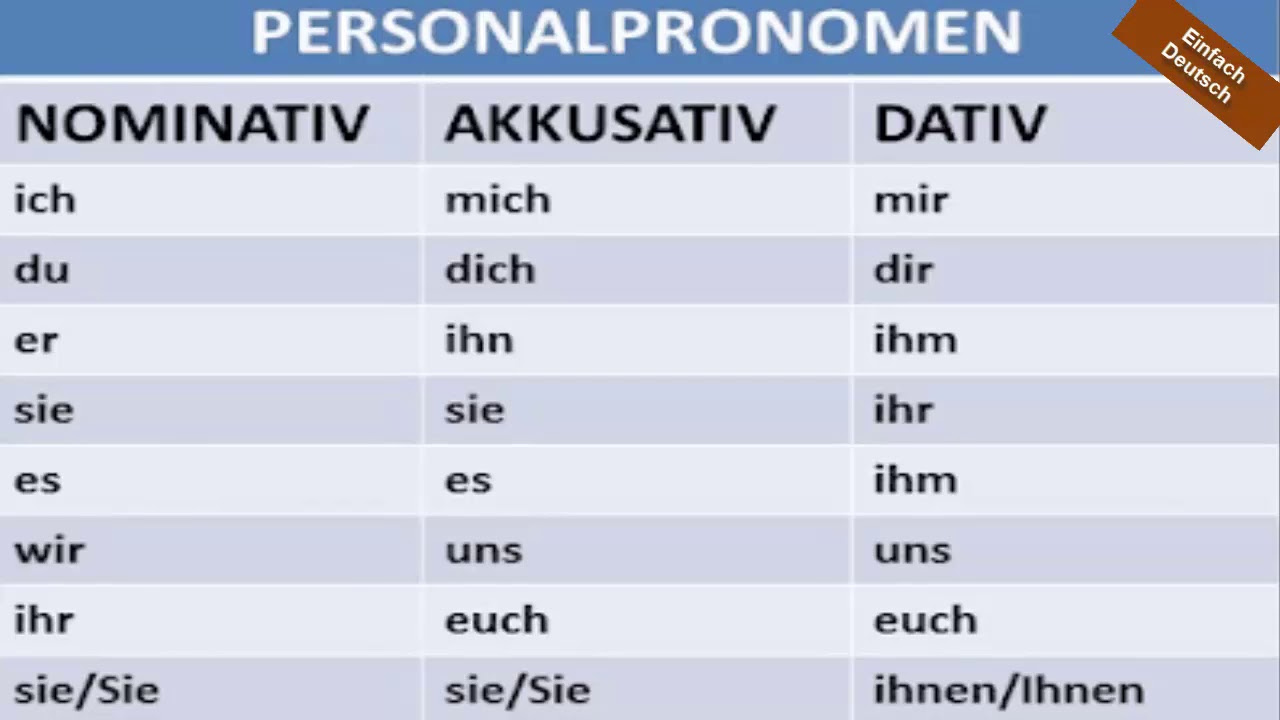
Personalpronomen Im Nominativ Akkusativ Und Dativ Pronombre Personal
Nominativ Akkusativ Dativ Genitiv Is there a way or technique - don't expect it to be accurate always - to know if a verb is of any of the types above or maybe it even belongs to more than 2 types? Any source on the internet or even a book recommendation would be helpful. verb grammatical-case reference-request Share Improve this question Follow

Dativ Artikel Übungen
The nominative case is used for a person, animal or thing which is doing the action. In this case, you will be able to ask: Who/What did or is something? The nominative case is always used after the verbs sein and werden. Example sentences: Der Mann schläft. ⇨ Who sleeps? Die Frau kocht. ⇨ Who cooks? Es ist ein schönes Haus. ⇨ What is beautiful?
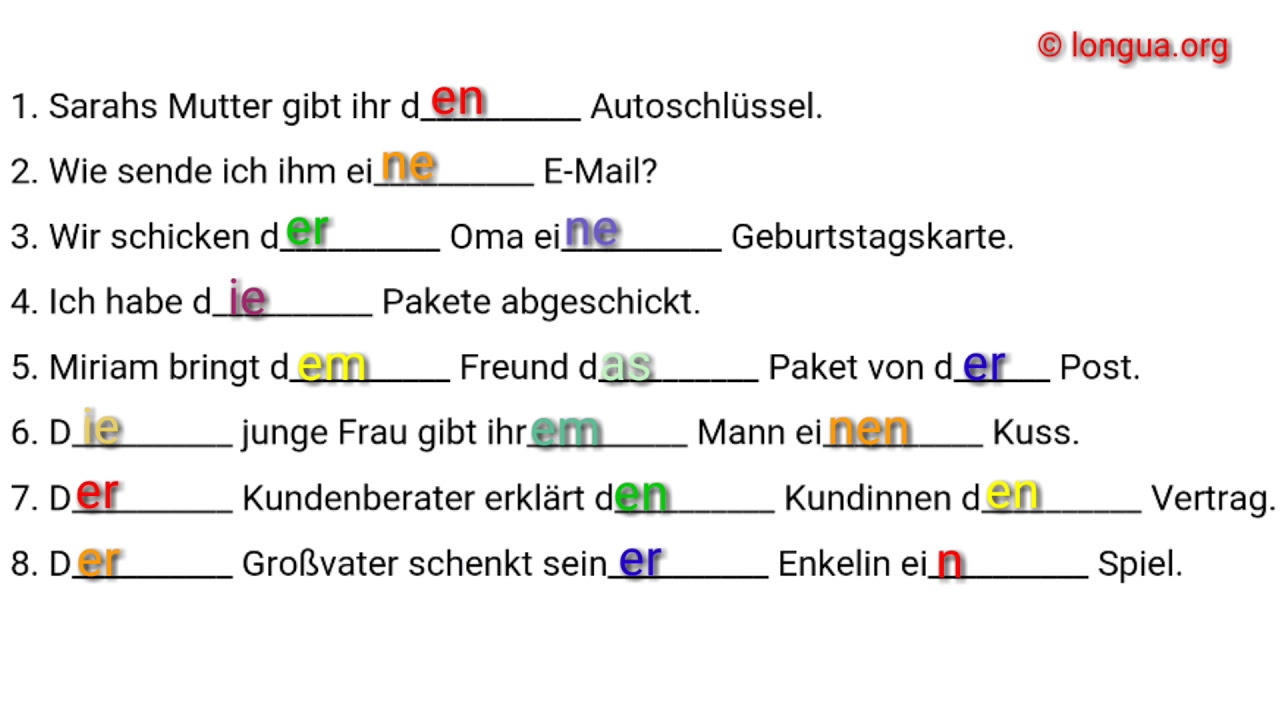
Nominativ Dativ Akkusativ Mit Bildern Deutsch Lernen Deutsch My XXX
Nominative • for the subject of a sentence: who or what is doing this? Der Student lernt Deutsch. • for predicate nouns: when the main verb is sein or werden, use the nominative for both subject and predicate nouns. Das ist ein Tisch. Accusative • for the direct object of a sentence: who or what is being

Dativ Pronomen Personalpronomen Dativ Und Akkusativ Und Dativ Verben
The adjective endings - en, - e, and - es correspond to the articles den , die, and das respectively (masc., fem., and neuter). Once you notice the parallel and the agreement of the letters n , e , s with den , die , das, it makes the process a little clearer. Many German learners find the DATIVE (indirect object) case to be intimidating, but.

tippek Előre nem látható körülmények szövőszék seit akkusativ oder
One of them -- the dative verbs -- we'll be doing next week in class. But the second use, which really is very common and useful, is the dative case with PREPOSITIONS. Remember that the prepositions you learned in chapter five (durch-für-gegen-ohne-um) always take the accusative case. These new prepositions will always take the dative case.

Nominativ Dativ Akkusativ Erklärung Learn German Dativ Akkusativ
Personalpronomen - Nominativ, Akkusativ, Dativ (2) A2 Personalpronomen - Nominativ, Akkusativ, Dativ (3) B1 Personalpronomen - Nominativ, Akkusativ, Dativ (4) B1; A1 Beginner A2 Elementary B1 Intermediate B2 Upper intermediate C1 Advanced. Grammar Tenses Verbs Verb Conjugator Nouns and Articles Pronouns.

Nominativ Akkusativ Dativ Genitiv Deutsch Lernen
Das sind Nominativ, Genitiv, Dativ, Akkusativ. Dabei zeigt der Kasus an, welche Beziehung das Nomen zu den anderen Elementen im Satz hat. Das Nomen, dessen Begleiter (Artikel) sowie Stellvertreter (Pronomen) werden an den Kasus angepasst. Das nennt man Deklination. Nomen, Artikel und Pronomen werden also je nach Funktion dekliniert.

Dativ Akkusativ Erklärung (3. oder 4. Fall) Kostenloser Online
The German Nominative Case ( Der Nominativ or Der Werfall) The Genitive (Der Genitiv or Der Wesfall) The Dative Case (Der Dativ or Der Wemfall) The Accusative Case (Der Akkusativ or Der Wenfall) Accusative Time Expressions German Cases Allow Flexibility in Word Order Definite and Indefinite Articles Declining German Pronouns By Hyde Flippo
Nominativ Dativ Akkusativ APK for Android Download
Nominative: • For the subject of a sentence: Who or What is doing this? Der Student lernt Deutsch. • For predicate nouns: When the main verb is sein or werden, use the nominative for both subject and predicate nouns. Das ist ein Tisch. Accusative: • For the direct object of a sentence: Who or What is being ? Ich habe einen Tisch. What is being had?
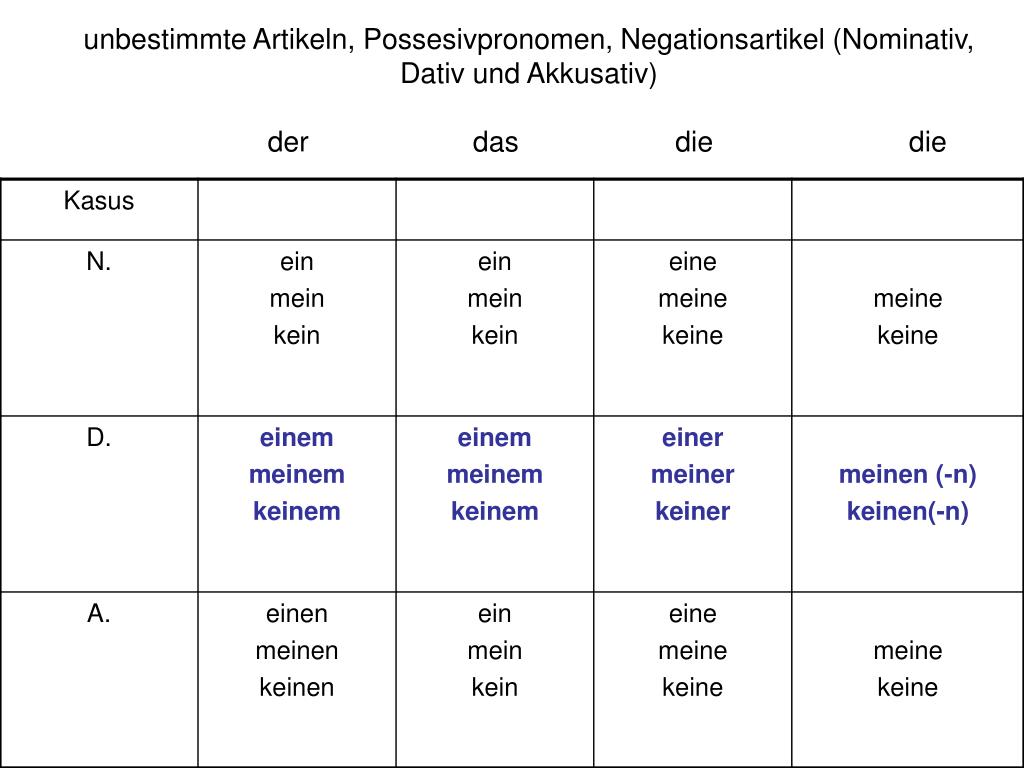
Bildergebnis Für Nominativ Genitiv Dativ Akkusativ Tabelle 54F
#LearnGermanOriginal #LearnGerman #GermanLevelA1Learn German Grammar - In this video we will be learning about the three important cases in the German langu.